Create a giottoPolygon object that is used to represent
spatial annotations and polygons. Inputs can be from a structured data.frame
object where three of the columns should correspond to x/y vertices and the
polygon ID and additional columns are set as attributes, a spatial file
such as wkt, .shp, or .GeoJSON, or a mask file (e.g. segmentation results).
The character method is for file reading and will dispatch to specific
methods based on what kind of data the file was.
Usage
# S4 method for class 'character'
createGiottoPolygon(
x,
remove_background_polygon = TRUE,
background_algo = "range",
make_valid = FALSE,
verbose = TRUE,
...
)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVector'
createGiottoPolygon(x, name = "cell", calc_centroids = FALSE, verbose = TRUE)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
createGiottoPolygon(
x,
name = "cell",
mask_method = c("guess", "single", "multiple"),
remove_background_polygon = FALSE,
background_algo = c("range"),
fill_holes = TRUE,
poly_IDs = NULL,
ID_fmt = "cell_",
flip_vertical = FALSE,
shift_vertical_step = FALSE,
flip_horizontal = FALSE,
shift_horizontal_step = FALSE,
remove_unvalid_polygons = TRUE,
calc_centroids = FALSE,
verbose = TRUE
)
# S4 method for class 'data.frame'
createGiottoPolygon(
x,
name = "cell",
part_col = NULL,
calc_centroids = FALSE,
skip_eval_dfr = FALSE,
copy_dt = TRUE,
verbose = TRUE,
make_valid = FALSE,
...
)
createGiottoPolygonsFromMask(
maskfile,
mask_method = c("guess", "single", "multiple"),
name = "cell",
remove_background_polygon = TRUE,
background_algo = c("range"),
fill_holes = TRUE,
poly_IDs = NULL,
ID_fmt = "cell_",
flip_vertical = FALSE,
shift_vertical_step = FALSE,
flip_horizontal = FALSE,
shift_horizontal_step = FALSE,
calc_centroids = FALSE,
remove_unvalid_polygons = TRUE,
verbose = FALSE
)
createGiottoPolygonsFromDfr(
segmdfr,
name = "cell",
part_col = NULL,
calc_centroids = FALSE,
make_valid = FALSE,
verbose = TRUE,
skip_eval_dfr = FALSE,
copy_dt = TRUE
)
createGiottoPolygonsFromGeoJSON(
GeoJSON,
name = "cell",
calc_centroids = FALSE,
make_valid = FALSE,
remove_background_polygon = TRUE,
background_algo = "range",
verbose = TRUE
)Arguments
- x
input. Filepath to a .GeoJSON or a mask image file. Can also be a data.frame with vertex 'x', 'y', and 'poly_ID' information.
- remove_background_polygon
try to remove background polygon (default: TRUE)
- background_algo
algorithm to remove background polygon
- make_valid
logical. (default
FALSE) Whether to runterra::makeValid()on the geometries. Setting this toTRUEmay cause read-in polygon attribute information to become out of sync.- verbose
be verbose
- ...
additional params to pass. For character method, params pass to SpatRaster or SpatVector methods, depending on whether x was a filepath to a maskfile or a spatial file (ex: wkt, shp, GeoJSON) respectively.
- name
character. Name to assign this set of polygons. This will also be the name of the spatial unit that they define. See giotto_schema
- calc_centroids
logical. (default
FALSE) calculate centroids for polygons- mask_method
how the mask file defines individual segmentation annotations. See mask_method section
- fill_holes
fill holes within created polygons
- poly_IDs
character vector. Default = NULL. Custom unique names for each polygon in the mask file.
- ID_fmt
character. Only applied if
poly_IDs = NULL. Naming scheme for poly_IDs. Default = "cell_". See ID_fmt section.- flip_vertical, flip_horizontal
logical. Flip output polygons across y (vertical) or x (horizontal) axis.
- shift_vertical_step, shift_horizontal_step
logical or numeric. When
FALSE, no shift is performed. When numeric, a shift of \(image height \times step\) (vertical) or \(image width \times step\) (horizontal) is performed.- remove_unvalid_polygons
remove unvalid polygons (default: TRUE)
- part_col
character (optional). If provided, a column in the data when processing will be indexed along as parts to generate a multipolygon.
- skip_eval_dfr
logical. (default FALSE) skip evaluation of provided dataframe
- copy_dt
(default TRUE) if segmdfr is provided as dt, this determines whether a copy is made
- maskfile
path to mask file, a terra
SpatRaster, or some other data class readable byterra::rast()- segmdfr
data.frame-like object with polygon coordinate information (x, y, poly_ID) with x and y being vertex information for the polygon referenced by poly_ID. See details for how columns are selected for coordinate and ID information.
- GeoJSON
path to .GeoJSON file
Details
When determining which column within tabular data is intended to
provide polygon information, Giotto first checks the column names for 'x',
'y', and 'poly_ID'. If any of these are discovered, they are directly
selected. If this is not discovered then Giotto checks the data type of the
columns and selects the first 'character' type column to be 'poly_ID' and
the first two 'numeric' columns as 'x' and 'y' respectively. If this is
also unsuccessful then poly_ID defaults to the 3rd column. 'x' and 'y' then
default to the 1st and 2nd columns.
mask_method
One of "single", "multiple", or "guess".
"single" assumes that the provided mask image is binary, with only polygon vs background being distinct values. With this kind of image, the expected generated polygons is a single multipart polygon. "single" takes this multipart polygon and breaks it apart into individual singlepart polygons. An initial simple
numericindex as the 'nth' polygon found in the mask image will be applied as an ID (see ID_fmt section)."multiple" assumes that the provided mask image has distinct intensity values to specify the IDs of individual polygons. An initial
numericID is applied as the intensity value of the pixels that made up the annotation for that polygon in the mask image (see ID_fmt section)."guess" examines the values in the image to pick the most likely appropriate method out of "single" or "multiple".
ID_fmt
Defaults to applying the input as a prefix (using paste0()) to the
numerical ID values detected by mask_method. (ie: ID_fmt = "cell_"
produces cell_1, cell_2, cell_3, ...)
If a "%" character is detected in the input then the input will be treated as
a sprintf() fmt param input instead. (ie: ID_fmt = "cell_%03d" produces
cell_001, cell_002, cell_003, ...)
Examples
# ------- create from a mask image ------- #
# example multi-value mask image
mask_multi <- system.file("extdata/toy_mask_multi.tif",
package = "GiottoClass"
)
plot(terra::rast(mask_multi), col = grDevices::hcl.colors(7)) # preview mask
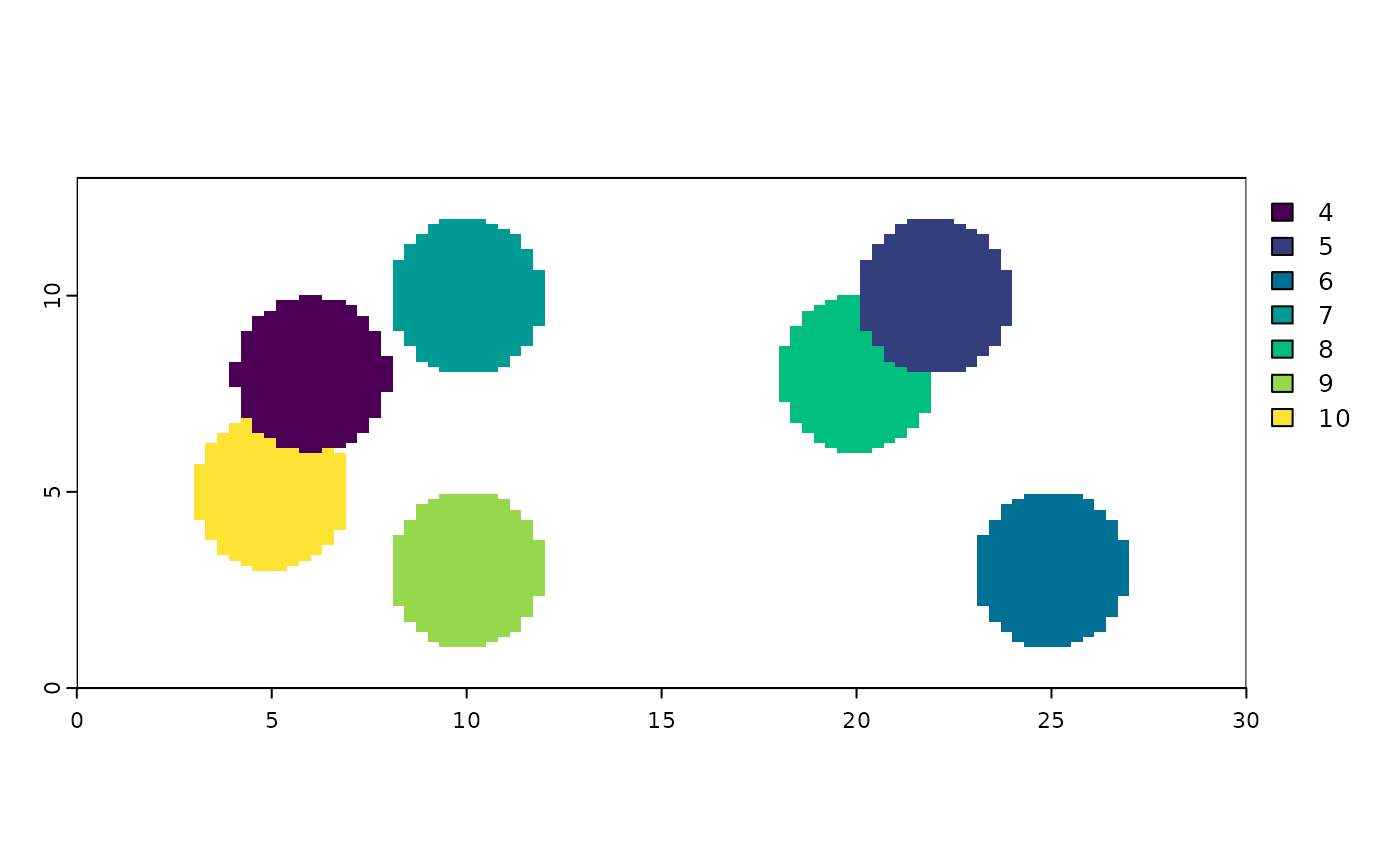 createGiottoPolygon(mask_multi) # with all default settings
#> An object of class giottoPolygon
#> spat_unit : "cell"
#> Spatial Information:
#> class : SpatVector
#> geometry : polygons
#> dimensions : 7, 1 (geometries, attributes)
#> extent : 3, 27, 1.04, 11.96 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. :
#> names : poly_ID
#> type : <chr>
#> values : cell_4
#> cell_5
#> cell_6
#> centroids : NULL
#> overlaps : NULL
gpoly1 <- createGiottoPolygon(mask_multi,
ID_fmt = "id_test_%03d", # apply a format when assigning poly_IDs
name = "multi_test"
)
force(gpoly1)
#> An object of class giottoPolygon
#> spat_unit : "multi_test"
#> Spatial Information:
#> class : SpatVector
#> geometry : polygons
#> dimensions : 7, 1 (geometries, attributes)
#> extent : 3, 27, 1.04, 11.96 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. :
#> names : poly_ID
#> type : <chr>
#> values : id_test_004
#> id_test_005
#> id_test_006
#> centroids : NULL
#> overlaps : NULL
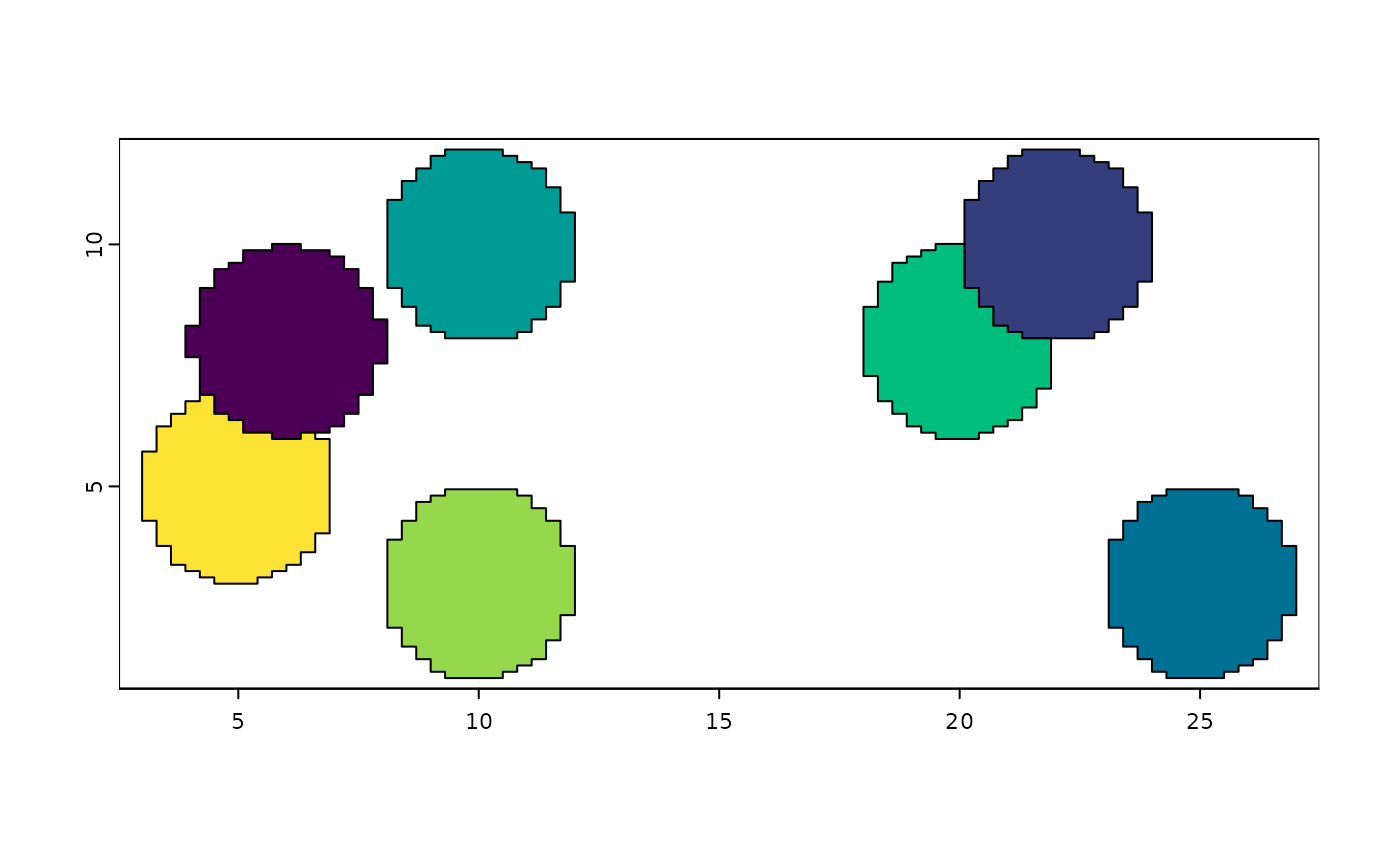
plot(gpoly1, col = grDevices::hcl.colors(7)) # plot poly
createGiottoPolygon(mask_multi) # with all default settings
#> An object of class giottoPolygon
#> spat_unit : "cell"
#> Spatial Information:
#> class : SpatVector
#> geometry : polygons
#> dimensions : 7, 1 (geometries, attributes)
#> extent : 3, 27, 1.04, 11.96 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. :
#> names : poly_ID
#> type : <chr>
#> values : cell_4
#> cell_5
#> cell_6
#> centroids : NULL
#> overlaps : NULL
gpoly1 <- createGiottoPolygon(mask_multi,
ID_fmt = "id_test_%03d", # apply a format when assigning poly_IDs
name = "multi_test"
)
force(gpoly1)
#> An object of class giottoPolygon
#> spat_unit : "multi_test"
#> Spatial Information:
#> class : SpatVector
#> geometry : polygons
#> dimensions : 7, 1 (geometries, attributes)
#> extent : 3, 27, 1.04, 11.96 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. :
#> names : poly_ID
#> type : <chr>
#> values : id_test_004
#> id_test_005
#> id_test_006
#> centroids : NULL
#> overlaps : NULL
plot(gpoly1, col = grDevices::hcl.colors(7)) # plot poly
 # example single-value mask image
mask_single <- system.file("extdata/toy_mask_single.tif",
package = "GiottoClass"
)
plot(terra::rast(mask_single)) # preview mask
# example single-value mask image
mask_single <- system.file("extdata/toy_mask_single.tif",
package = "GiottoClass"
)
plot(terra::rast(mask_single)) # preview mask
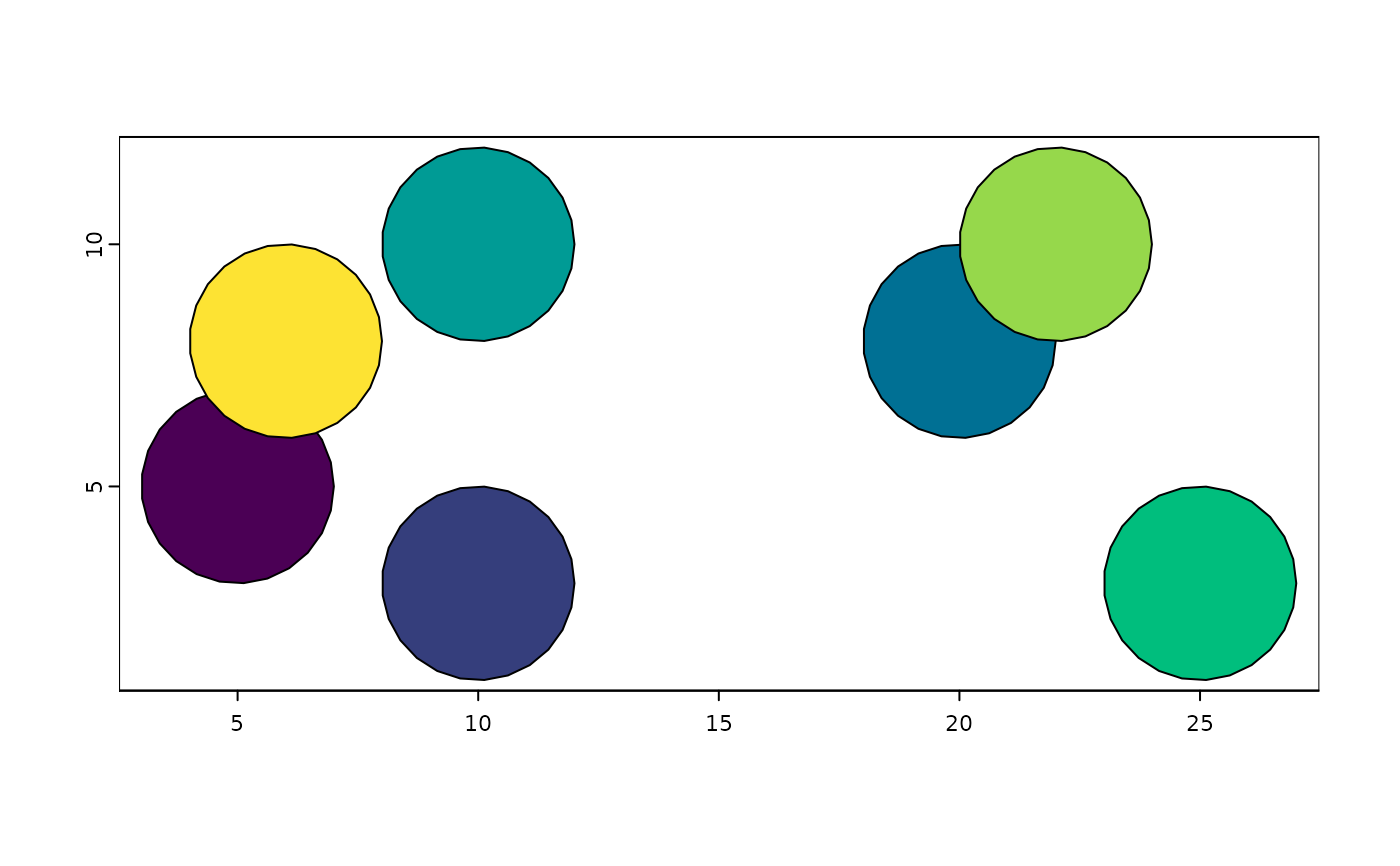 gpoly2 <- createGiottoPolygon(mask_single,
ID_fmt = "id_test_%03d",
name = "single_test"
)
#> Selecting col "part" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(gpoly2, col = grDevices::hcl.colors(5)) # plot poly
gpoly2 <- createGiottoPolygon(mask_single,
ID_fmt = "id_test_%03d",
name = "single_test"
)
#> Selecting col "part" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(gpoly2, col = grDevices::hcl.colors(5)) # plot poly
 # ------- create from an shp file ------- #
shp <- system.file("extdata/toy_poly.shp", package = "GiottoClass")
# vector inputs do not have params for flipping and shifting
gp2 <- createGiottoPolygon(shp)
#> Selecting attribute "poly_ID" as poly_ID
#> Selecting attribute "poly_ID" as poly_ID
plot(gp2, col = grDevices::hcl.colors(7))
# ------- create from an shp file ------- #
shp <- system.file("extdata/toy_poly.shp", package = "GiottoClass")
# vector inputs do not have params for flipping and shifting
gp2 <- createGiottoPolygon(shp)
#> Selecting attribute "poly_ID" as poly_ID
#> Selecting attribute "poly_ID" as poly_ID
plot(gp2, col = grDevices::hcl.colors(7))
 # ------- create from data.frame-like ------- #
# load example data and convert to data.table
dt <- data.table::data.table(
id = c(
rep('a', 3), # Triangle (id 'a')
rep('b', 4), # Square 1 (id 'b')
rep('c', 4) # Square 2 (id 'c')
),
x = c(
0, 1, 0.5,
2, 5, 5, 2,
6, 7, 7, 6
),
y = c(
0, 0, 1,
2, 2, 5, 5,
5, 5, 6, 6
)
)
# simple polygons only need 3 cols
force(dt)
#> id x y
#> <char> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0
#> 2: a 1.0 0
#> 3: a 0.5 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2
#> 5: b 5.0 2
#> 6: b 5.0 5
#> 7: b 2.0 5
#> 8: c 6.0 5
#> 9: c 7.0 5
#> 10: c 7.0 6
#> 11: c 6.0 6
out1 <- createGiottoPolygon(dt)
#> Selecting col "id" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(out1, col = getRainbowColors(3))
# ------- create from data.frame-like ------- #
# load example data and convert to data.table
dt <- data.table::data.table(
id = c(
rep('a', 3), # Triangle (id 'a')
rep('b', 4), # Square 1 (id 'b')
rep('c', 4) # Square 2 (id 'c')
),
x = c(
0, 1, 0.5,
2, 5, 5, 2,
6, 7, 7, 6
),
y = c(
0, 0, 1,
2, 2, 5, 5,
5, 5, 6, 6
)
)
# simple polygons only need 3 cols
force(dt)
#> id x y
#> <char> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0
#> 2: a 1.0 0
#> 3: a 0.5 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2
#> 5: b 5.0 2
#> 6: b 5.0 5
#> 7: b 2.0 5
#> 8: c 6.0 5
#> 9: c 7.0 5
#> 10: c 7.0 6
#> 11: c 6.0 6
out1 <- createGiottoPolygon(dt)
#> Selecting col "id" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(out1, col = getRainbowColors(3))
 # multipolygons can be generated using the `part_col` param
dt[, part_index := c(rep(1, 7), rep(2, 4))]
#> id x y part_index
#> <char> <num> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0 1
#> 2: a 1.0 0 1
#> 3: a 0.5 1 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2 1
#> 5: b 5.0 2 1
#> 6: b 5.0 5 1
#> 7: b 2.0 5 1
#> 8: c 6.0 5 2
#> 9: c 7.0 5 2
#> 10: c 7.0 6 2
#> 11: c 6.0 6 2
dt[, id := c(rep("a", 3), rep("b", 8))]
#> id x y part_index
#> <char> <num> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0 1
#> 2: a 1.0 0 1
#> 3: a 0.5 1 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2 1
#> 5: b 5.0 2 1
#> 6: b 5.0 5 1
#> 7: b 2.0 5 1
#> 8: b 6.0 5 2
#> 9: b 7.0 5 2
#> 10: b 7.0 6 2
#> 11: b 6.0 6 2
force(dt)
#> id x y part_index
#> <char> <num> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0 1
#> 2: a 1.0 0 1
#> 3: a 0.5 1 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2 1
#> 5: b 5.0 2 1
#> 6: b 5.0 5 1
#> 7: b 2.0 5 1
#> 8: b 6.0 5 2
#> 9: b 7.0 5 2
#> 10: b 7.0 6 2
#> 11: b 6.0 6 2
out2 <- createGiottoPolygon(dt, part_col = "part_index")
#> Selecting col "id" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(out2, col = getRainbowColors(2))
# multipolygons can be generated using the `part_col` param
dt[, part_index := c(rep(1, 7), rep(2, 4))]
#> id x y part_index
#> <char> <num> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0 1
#> 2: a 1.0 0 1
#> 3: a 0.5 1 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2 1
#> 5: b 5.0 2 1
#> 6: b 5.0 5 1
#> 7: b 2.0 5 1
#> 8: c 6.0 5 2
#> 9: c 7.0 5 2
#> 10: c 7.0 6 2
#> 11: c 6.0 6 2
dt[, id := c(rep("a", 3), rep("b", 8))]
#> id x y part_index
#> <char> <num> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0 1
#> 2: a 1.0 0 1
#> 3: a 0.5 1 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2 1
#> 5: b 5.0 2 1
#> 6: b 5.0 5 1
#> 7: b 2.0 5 1
#> 8: b 6.0 5 2
#> 9: b 7.0 5 2
#> 10: b 7.0 6 2
#> 11: b 6.0 6 2
force(dt)
#> id x y part_index
#> <char> <num> <num> <num>
#> 1: a 0.0 0 1
#> 2: a 1.0 0 1
#> 3: a 0.5 1 1
#> 4: b 2.0 2 1
#> 5: b 5.0 2 1
#> 6: b 5.0 5 1
#> 7: b 2.0 5 1
#> 8: b 6.0 5 2
#> 9: b 7.0 5 2
#> 10: b 7.0 6 2
#> 11: b 6.0 6 2
out2 <- createGiottoPolygon(dt, part_col = "part_index")
#> Selecting col "id" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(out2, col = getRainbowColors(2))
 # For more complex inputs with holes, it is recommended to format into
# the geom, part, x, y, hole, format that terra uses with matrix inputs
# + poly_ID.
# extract 5 column representation:
dt_full <- data.table::as.data.table(out2, geom = "XY")
force(dt_full)
#> Key: <geom>
#> geom part x y hole poly_ID
#> <int> <num> <num> <num> <num> <char>
#> 1: 1 1 0.0 0 0 a
#> 2: 1 1 1.0 0 0 a
#> 3: 1 1 0.5 1 0 a
#> 4: 1 1 0.0 0 0 a
#> 5: 2 1 2.0 2 0 b
#> 6: 2 1 5.0 2 0 b
#> 7: 2 1 5.0 5 0 b
#> 8: 2 1 2.0 5 0 b
#> 9: 2 1 2.0 2 0 b
#> 10: 2 2 6.0 5 0 b
#> 11: 2 2 7.0 5 0 b
#> 12: 2 2 7.0 6 0 b
#> 13: 2 2 6.0 6 0 b
#> 14: 2 2 6.0 5 0 b
# Columns named geom, part, x, y, hole, are treated specially when provided.
# They can be directly used without internal modification
res <- createGiottoPolygon(dt_full)
#> Selecting col "poly_ID" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(res, col = getRainbowColors(2))
# additional columns outside of the 3 (+ part_col if provided) or 5 column
# formatting are retained as attributes
# These cols MUST map with the poly_ID/geom.
# set up an example attribute
dt_full$attribute <- match(dt_full$poly_ID, letters)
createGiottoPolygon(dt_full)
#> Selecting col "poly_ID" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
#> An object of class giottoPolygon
#> spat_unit : "cell"
#> Spatial Information:
#> class : SpatVector
#> geometry : polygons
#> dimensions : 2, 2 (geometries, attributes)
#> extent : 0, 7, 0, 6 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. :
#> names : poly_ID attribute
#> type : <chr> <int>
#> values : a 1
#> b 2
#> centroids : NULL
#> overlaps : NULL
# For more complex inputs with holes, it is recommended to format into
# the geom, part, x, y, hole, format that terra uses with matrix inputs
# + poly_ID.
# extract 5 column representation:
dt_full <- data.table::as.data.table(out2, geom = "XY")
force(dt_full)
#> Key: <geom>
#> geom part x y hole poly_ID
#> <int> <num> <num> <num> <num> <char>
#> 1: 1 1 0.0 0 0 a
#> 2: 1 1 1.0 0 0 a
#> 3: 1 1 0.5 1 0 a
#> 4: 1 1 0.0 0 0 a
#> 5: 2 1 2.0 2 0 b
#> 6: 2 1 5.0 2 0 b
#> 7: 2 1 5.0 5 0 b
#> 8: 2 1 2.0 5 0 b
#> 9: 2 1 2.0 2 0 b
#> 10: 2 2 6.0 5 0 b
#> 11: 2 2 7.0 5 0 b
#> 12: 2 2 7.0 6 0 b
#> 13: 2 2 6.0 6 0 b
#> 14: 2 2 6.0 5 0 b
# Columns named geom, part, x, y, hole, are treated specially when provided.
# They can be directly used without internal modification
res <- createGiottoPolygon(dt_full)
#> Selecting col "poly_ID" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
plot(res, col = getRainbowColors(2))
# additional columns outside of the 3 (+ part_col if provided) or 5 column
# formatting are retained as attributes
# These cols MUST map with the poly_ID/geom.
# set up an example attribute
dt_full$attribute <- match(dt_full$poly_ID, letters)
createGiottoPolygon(dt_full)
#> Selecting col "poly_ID" as poly_ID column
#> Selecting cols "x" and "y" as x and y respectively
#> An object of class giottoPolygon
#> spat_unit : "cell"
#> Spatial Information:
#> class : SpatVector
#> geometry : polygons
#> dimensions : 2, 2 (geometries, attributes)
#> extent : 0, 7, 0, 6 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
#> coord. ref. :
#> names : poly_ID attribute
#> type : <chr> <int>
#> values : a 1
#> b 2
#> centroids : NULL
#> overlaps : NULL
