identify significant prinicipal components (PCs)
signPCA(
gobject,
feat_type = NULL,
spat_unit = NULL,
name = NULL,
method = c("screeplot", "jackstraw"),
expression_values = c("normalized", "scaled", "custom"),
reduction = c("cells", "feats"),
pca_method = c("irlba", "factominer"),
rev = FALSE,
feats_to_use = NULL,
center = TRUE,
scale_unit = TRUE,
ncp = 50,
scree_ylim = c(0, 10),
jack_iter = 10,
jack_threshold = 0.01,
jack_ylim = c(0, 1),
verbose = TRUE,
show_plot = NULL,
return_plot = NULL,
save_plot = NULL,
save_param = list(),
default_save_name = "signPCA"
)Arguments
- gobject
giotto object
- feat_type
feature type (e.g. "rna", "dna", "protein")
- spat_unit
spatial unit (e.g. "cell")
- name
name of PCA object if available
- method
method to use to identify significant PCs
- expression_values
expression values to use
- reduction
cells or genes
- pca_method
which implementation to use
- rev
do a reverse PCA
- feats_to_use
subset of features to use for PCA
- center
center data before PCA
- scale_unit
scale features before PCA
- ncp
number of principal components to calculate
- scree_ylim
y-axis limits on scree plot
- jack_iter
number of interations for jackstraw
- jack_threshold
p-value threshold to call a PC significant
- jack_ylim
y-axis limits on jackstraw plot
- verbose
be verbose
- show_plot
logical. show plot
- return_plot
logical. return ggplot object
- save_plot
logical. save the plot
- save_param
list of saving parameters, see
showSaveParameters- default_save_name
default save name for saving, don't change, change save_name in save_param
Value
ggplot object for scree method and maxtrix of p-values for jackstraw
Details
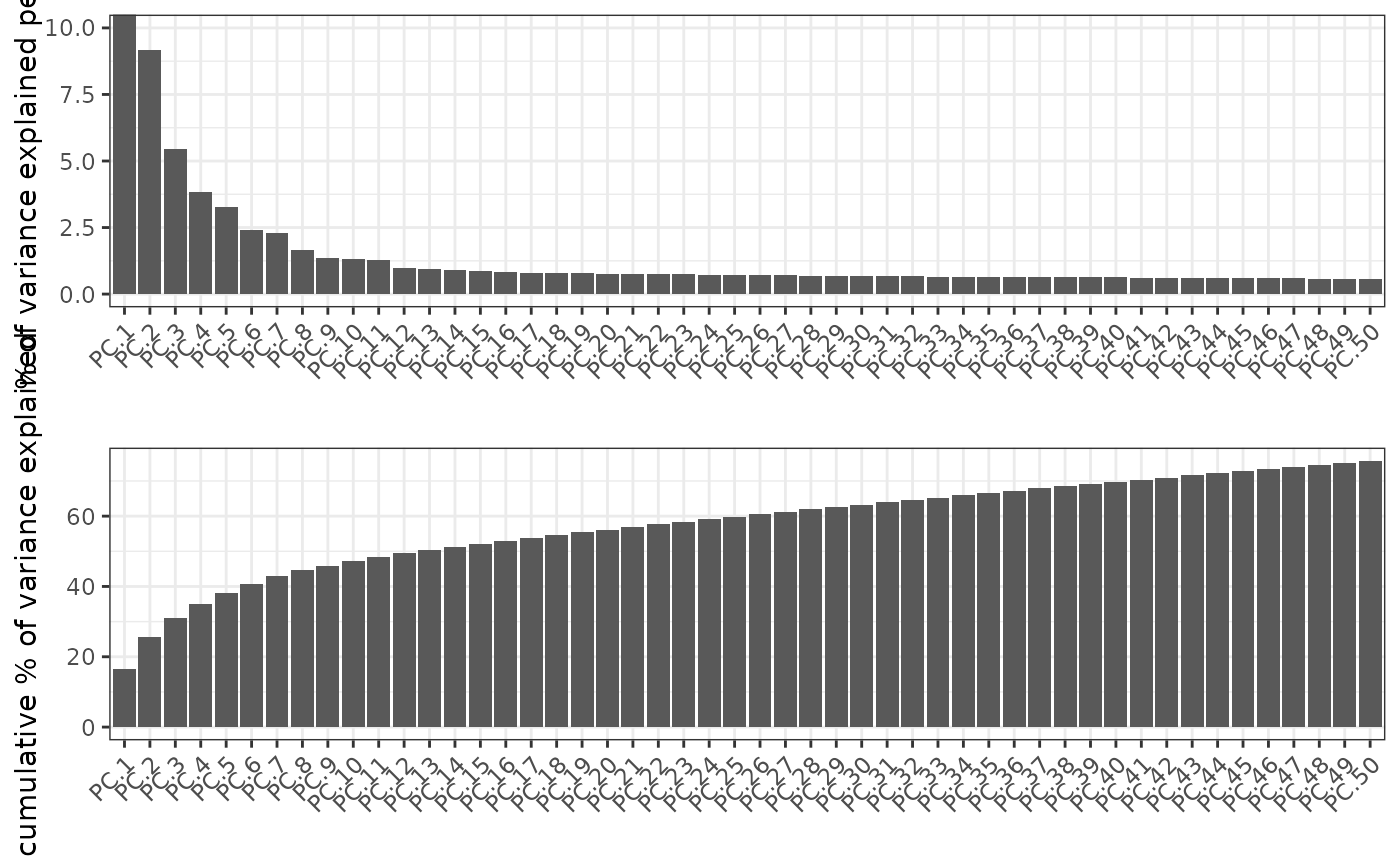
Two different methods can be used to assess the number of relevant
or significant prinicipal components (PC's).
1. Screeplot works by plotting the explained variance of each
individual PC in a barplot allowing you to identify which PC provides a
significant
contribution (a.k.a. 'elbow method').
2. The Jackstraw method uses the permutationPA
function. By systematically permuting genes it identifies robust, and thus
significant, PCs.
Examples
g <- GiottoData::loadGiottoMini("visium")
#> 1. read Giotto object
#> 2. read Giotto feature information
#> 3. read Giotto spatial information
#> 3.1 read Giotto spatial shape information
#> 3.2 read Giotto spatial centroid information
#> 3.3 read Giotto spatial overlap information
#> 4. read Giotto image information
#> python already initialized in this session
#> active environment : '/usr/bin/python3'
#> python version : 3.12
signPCA(g)
#> Warning: The `name` argument of `screePlot()` is deprecated as of Giotto 4.1.1.
#> ℹ Please use the `dim_reduction_name` argument instead.
#> ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the Giotto package.
#> Please report the issue at <https://github.com/drieslab/Giotto/issues>.
#> PCA with name: pca already exists and will be used for the screeplot