Resolve Bioscience Breast Cancer Subcellular
Source:vignettes/resolve_biosciences.Rmd
resolve_biosciences.Rmd
# Ensure Giotto Suite is installed.
if (!"Giotto" %in% installed.packages()) {
pak::pkg_install("drieslab/Giotto")
}
# Ensure GiottoData, a small, helper module for tutorials, is installed.
if (!"GiottoData" %in% installed.packages()) {
pak::pkg_install("drieslab/GiottoData")
}
# Ensure the Python environment for Giotto has been installed.
genv_exists <- Giotto::checkGiottoEnvironment()
if (!genv_exists) {
# The following command need only be run once to install the Giotto environment.
Giotto::installGiottoEnvironment()
}1 Start Giotto
library(Giotto)
library(GiottoData)
# 1. set working directory
my_working_dir <- getwd()
# Optional: Specify a path to a Python executable within a conda or miniconda
# environment. If set to NULL (default), the Python executable within the previously
# installed Giotto environment will be used.
python_path <- NULL # alternatively, "/local/python/path/python" if desired.2 Input Files
## provide path to resolve bioscience folder
data_path <- "/path/to/data/"
# 1. original image as png
original_DAPI_image <- paste0(data_path, "/sample2_DAPI.jpg")
# 2. input cell segmentation as mask file
# can also be provided as a 3-column polygon file
# to be used as image background AND to store segmentations as polygons
# can be obtained through Fiji / QuPath / Ilastik / Cellpose / ...
segmentation_mask <- paste0(data_path, "/Mask3.png")
# 3. input features coordinates
tx_coord <- fread(paste0(data_path, "/data_sample2.txt"))
colnames(tx_coord) <- c("x", "y", "z", "gene_id")
tx_coord <- tx_coord[, .(x, y, gene_id)]3 Create Subcellular Giotto Object
results_folder <- "/path/to/results/"
instructions <- createGiottoInstructions(
save_plot = TRUE,
show_plot = FALSE,
return_plot = FALSE,
save_dir = results_folder,
python_path = NULL
)
testobj <- createGiottoObjectSubcellular(gpoints = list("rna" = tx_coord),
gpolygons = list("cell" = segmentation_mask),
instructions = instructions,
verbose = FALSE,
cores = 32
)4 Create Spatial Locations
# centroids are now used to provide the spatial locations (centroid of each cell)
# needed for certain downstream spatial analyses
testobj <- addSpatialCentroidLocations(testobj,
poly_info = "cell"
)5 Add Image Information
# create Giotto images
DAPI_image <- createGiottoImage(gobject = testobj,
name = "DAPI",
do_manual_adj = TRUE,
xmax_adj = 0, ymax_adj = 0,
xmin_adj = 0, ymin_adj = 0,
image_transformations = "flip_x_axis",
mg_object = original_DAPI_image
)
segm_image <- createGiottoImage(gobject = testobj,
name = "segmentation",
do_manual_adj = TRUE,
xmax_adj = 0, ymax_adj = 0,
xmin_adj = 0, ymin_adj = 0,
image_transformations = "flip_x_axis",
mg_object = segmentation_mask
)
# add images to Giotto object
testobj <- addGiottoImage(testobj,
images = list(DAPI_image, segm_image)
)
# provides an overview of available images
showGiottoImageNames(testobj)6 Visualize Original Images
# visualize overlay of calculated cell centroid with original image and segmentation mask file
# by setting show_plot to FALSE and save_plot to TRUE you can save quite some time when creating plots
# with big images it sometimes takes quite long for R/Rstudio to render them
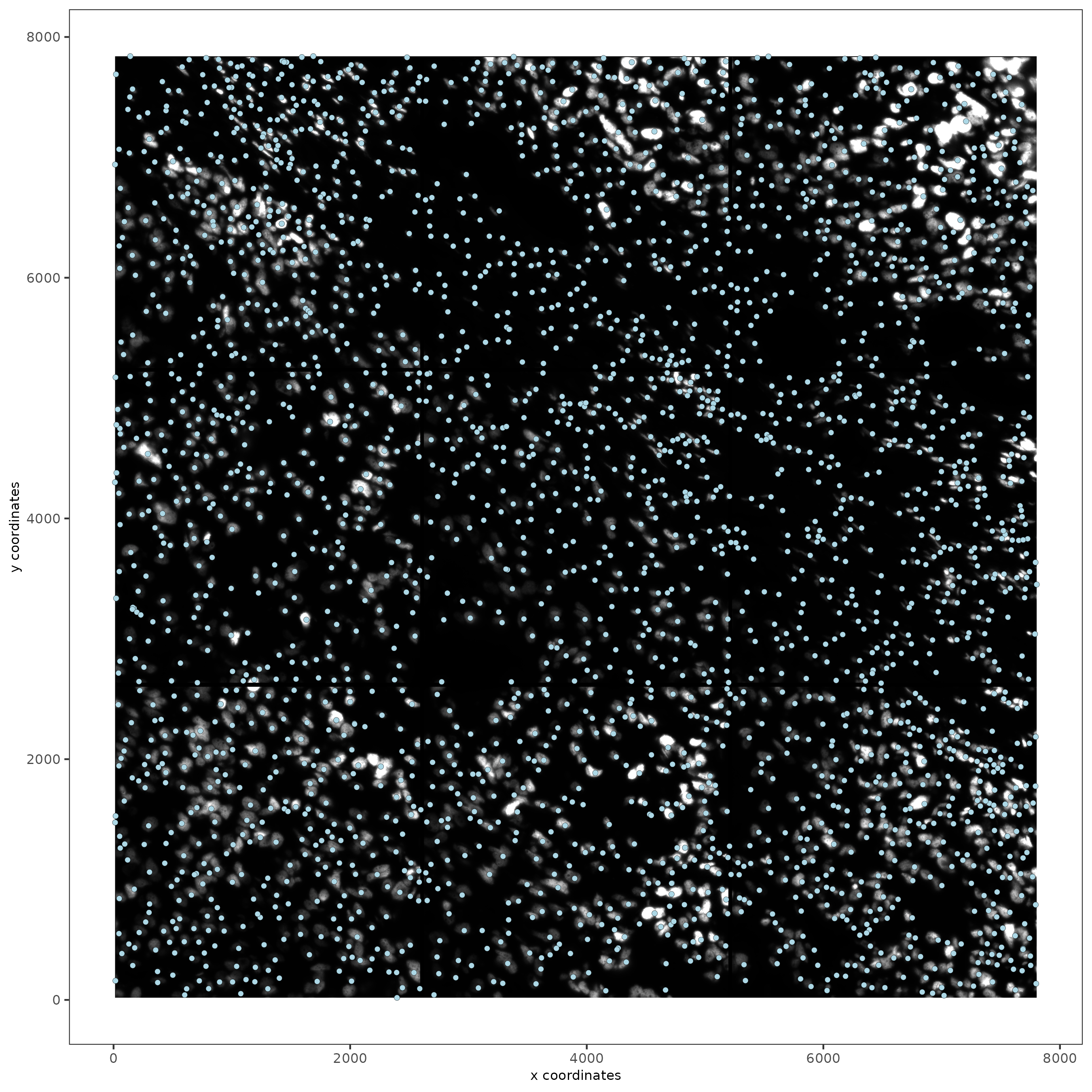
spatPlot2D(gobject = testobj,
image_name = "DAPI",
point_size = 1.5
)
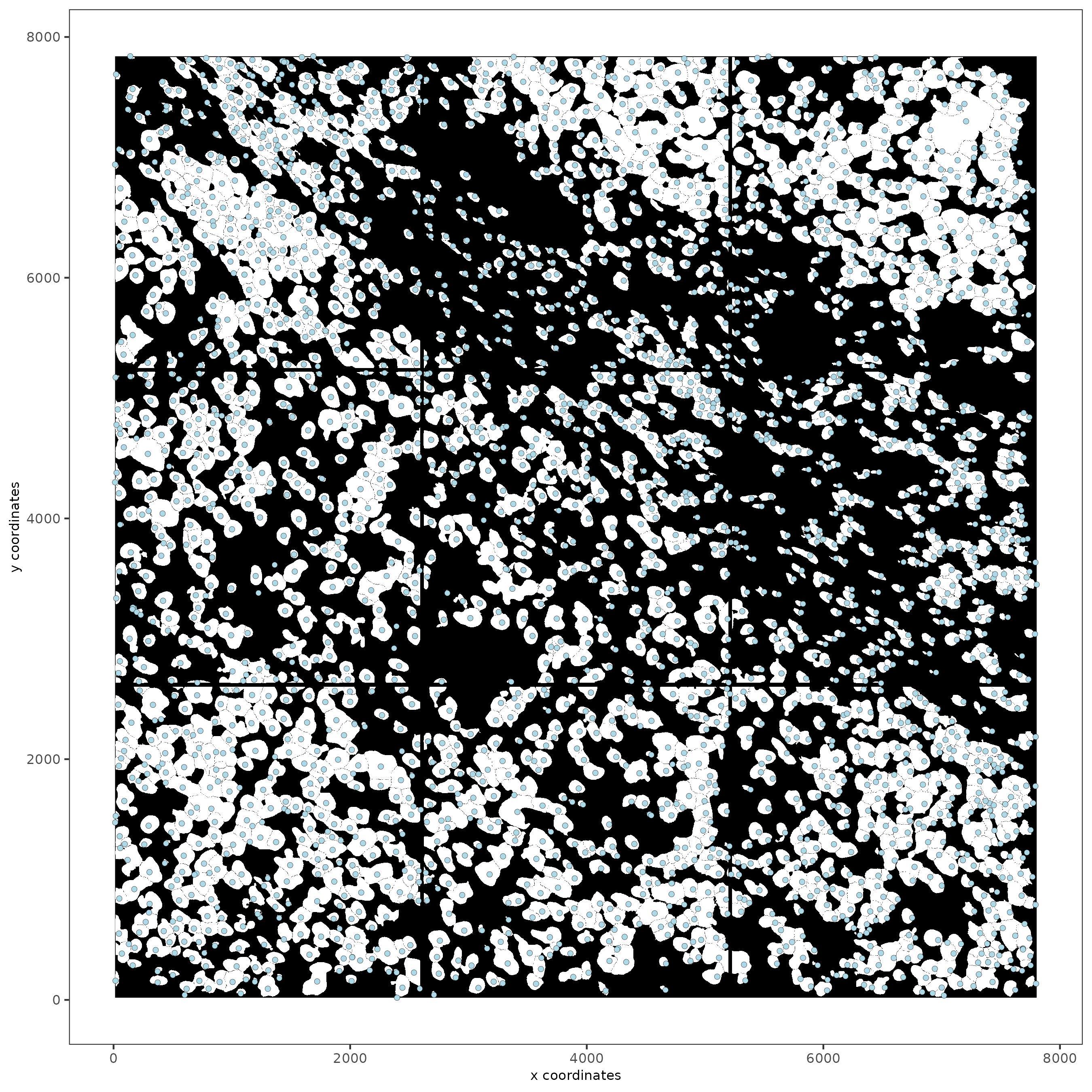
spatPlot2D(gobject = testobj,
image_name = "segmentation",
point_size = 1.5
)
7 Calculate Cell Shape Overlap
tictoc::tic()
testobj <- calculateOverlap(testobj,
method = "parallel",
x_step = 1000,
y_step = 1000,
poly_info = "cell",
feat_info = "rna"
)
tictoc::toc()
# convert overlap to matrix
testobj <- overlapToMatrix(testobj,
poly_info = "cell",
feat_info = "rna",
name = "raw"
)8 Filter Data
# features can be filtered individually
# cells will be filtered across features
# first filter on rna
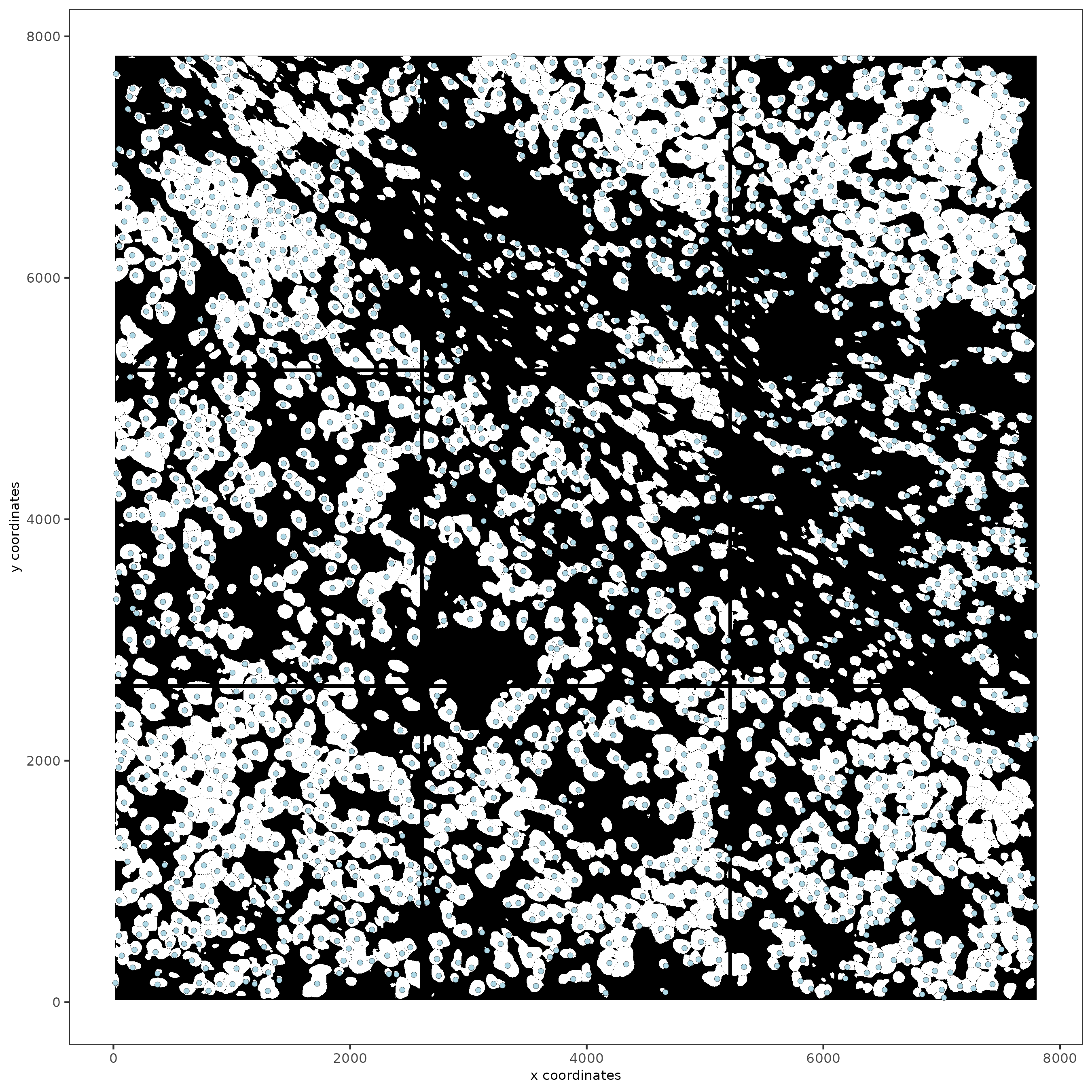
subc_test <- filterGiotto(gobject = testobj,
expression_threshold = 1,
feat_det_in_min_cells = 20,
min_det_feats_per_cell = 5
)
spatPlot2D(gobject = subc_test,
image_name = "segmentation",
show_image = TRUE,
point_size = 1.5
)
9 Process Giotto Object
# rna data, default.
# other feature modalities can be processed and filtered in an anologous manner
subc_test <- normalizeGiotto(gobject = subc_test,
scalefactor = 6000,
verbose = TRUE
)
subc_test <- addStatistics(gobject = subc_test)
subc_test <- adjustGiottoMatrix(gobject = subc_test,
expression_values = "normalized",
covariate_columns = c("nr_feats", "total_expr")
)
subc_test <- normalizeGiotto(gobject = subc_test,
norm_methods = "pearson_resid",
update_slot = "pearson")
showGiottoExpression(subc_test)10 Dimension Reduction
# Find highly valuable Features
# typical way of calculating HVF
subc_test <- calculateHVF(gobject = subc_test,
HVFname = "hvg_orig")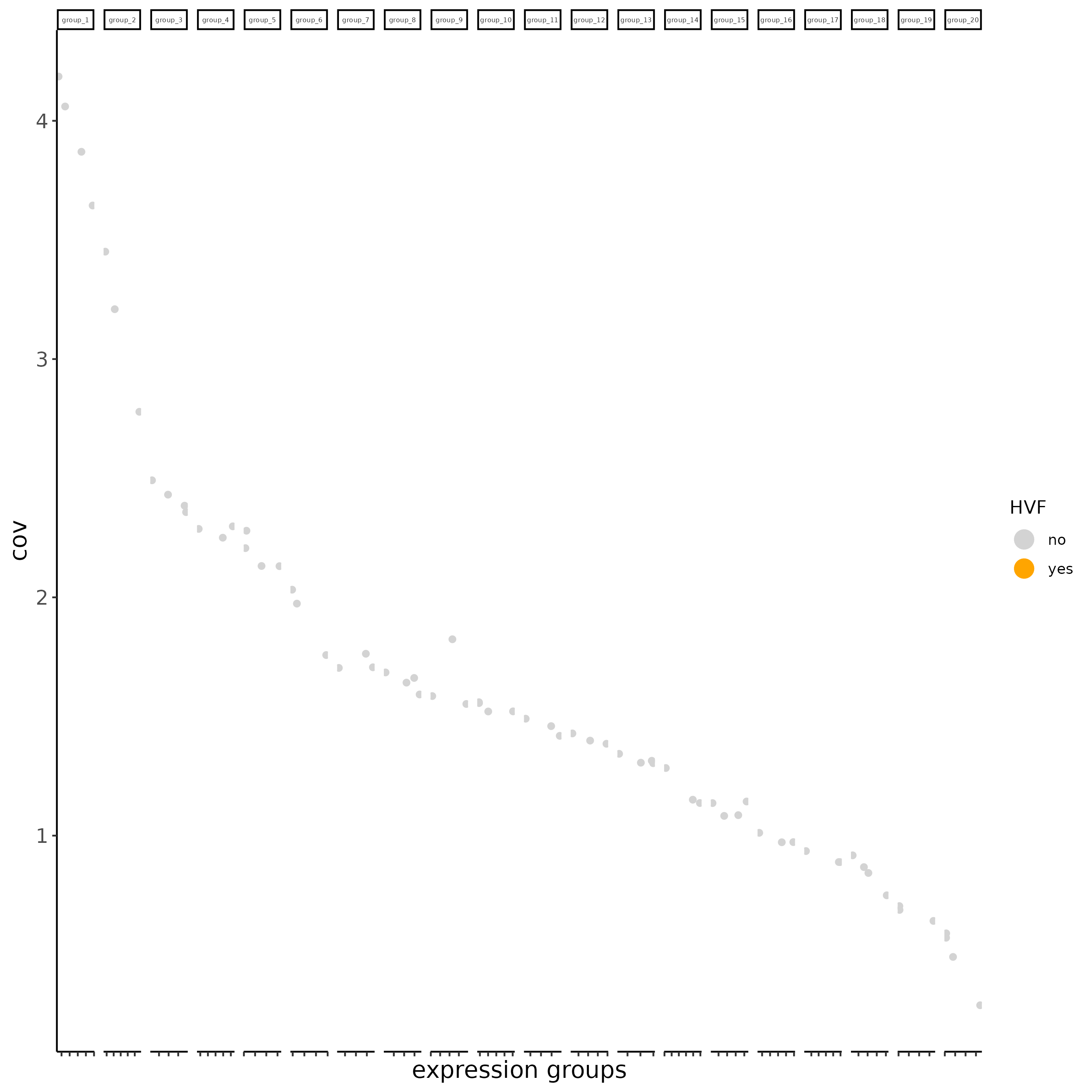
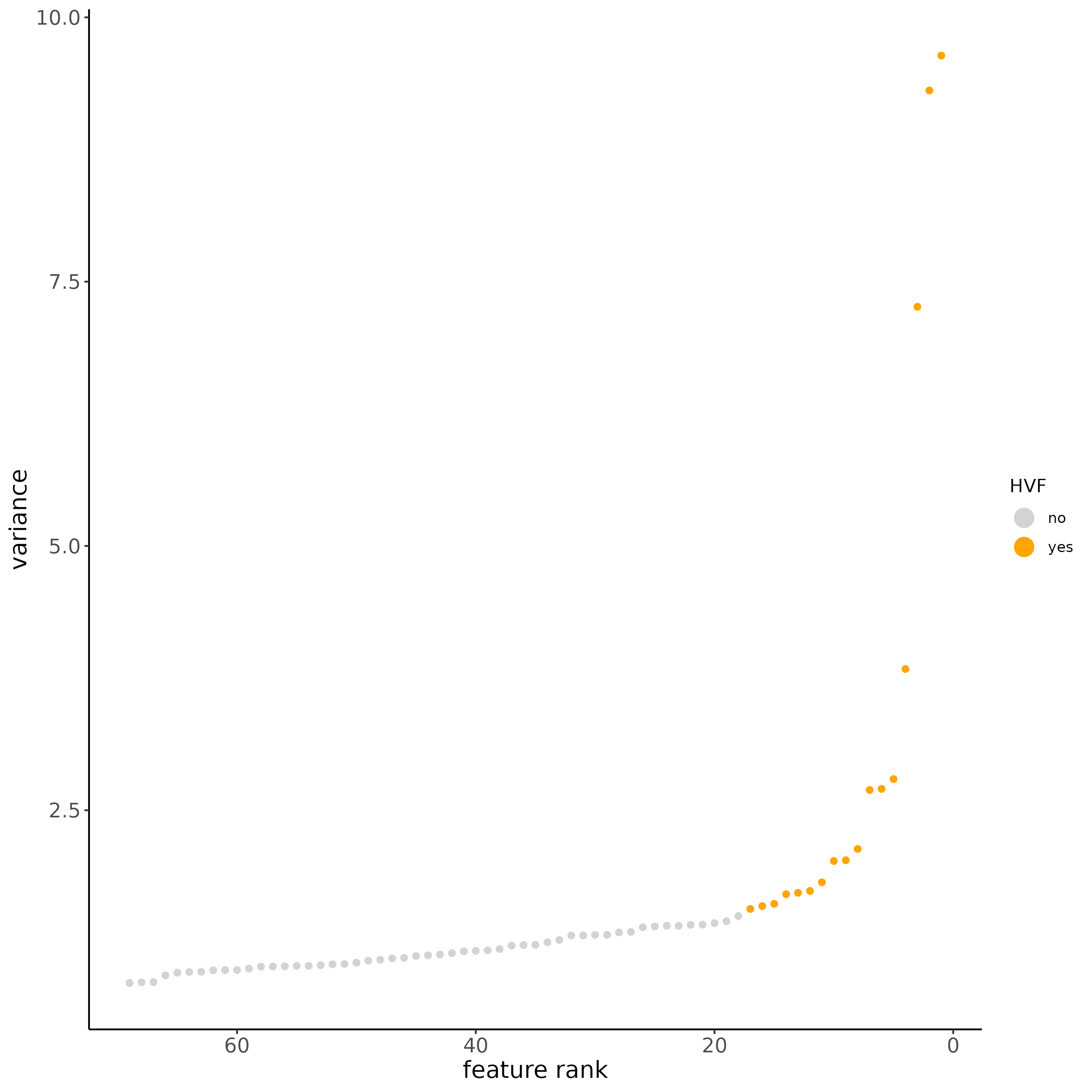
# new method based on variance of pearson residuals for each gene
subc_test <- calculateHVF(gobject = subc_test,
method = "var_p_resid",
expression_values = "pearson",
show_plot = TRUE
)
# run PCA
subc_test <- runPCA(gobject = subc_test,
expression_values = "pearson",
scale_unit = FALSE,
center = FALSE
)
screePlot(subc_test, ncp = 20)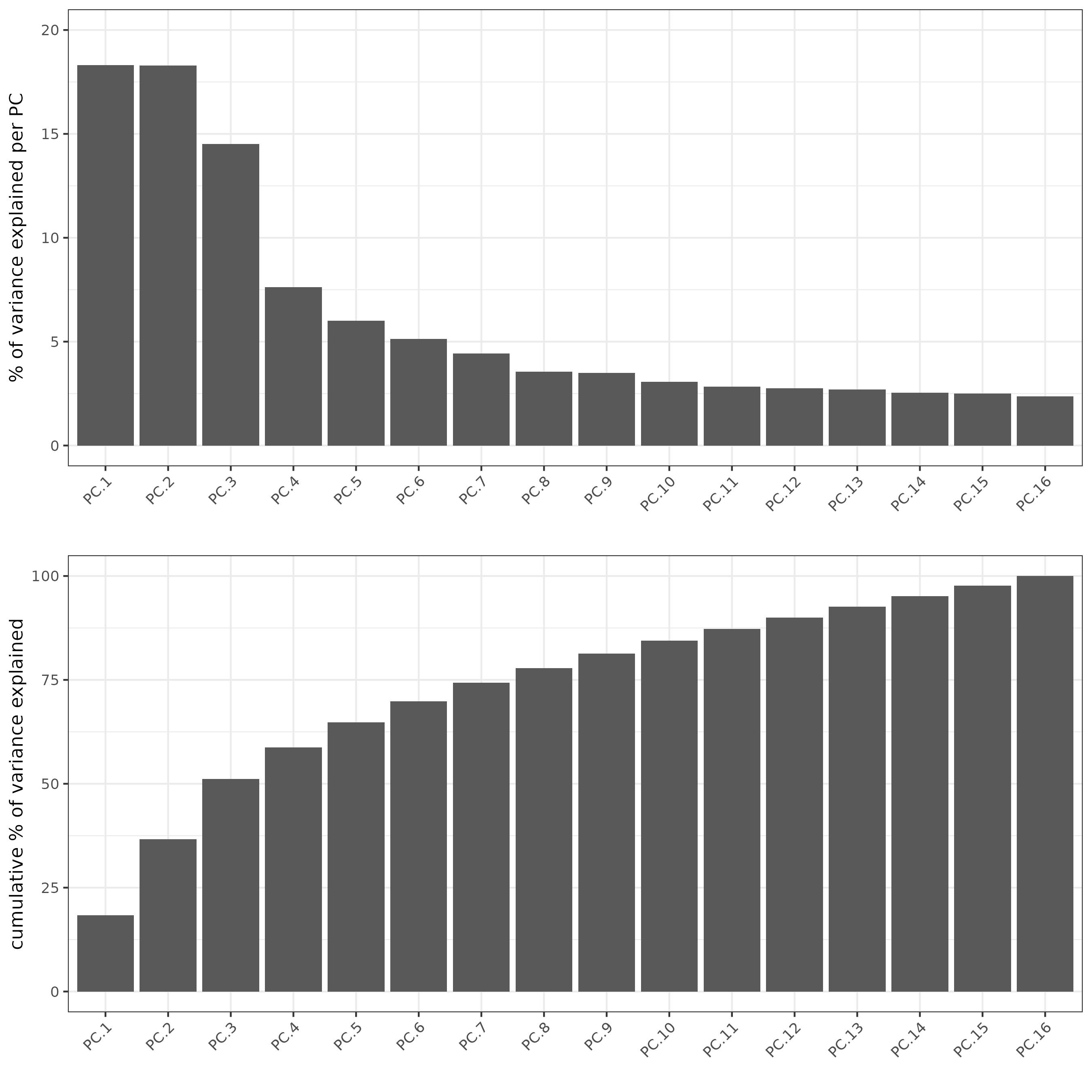
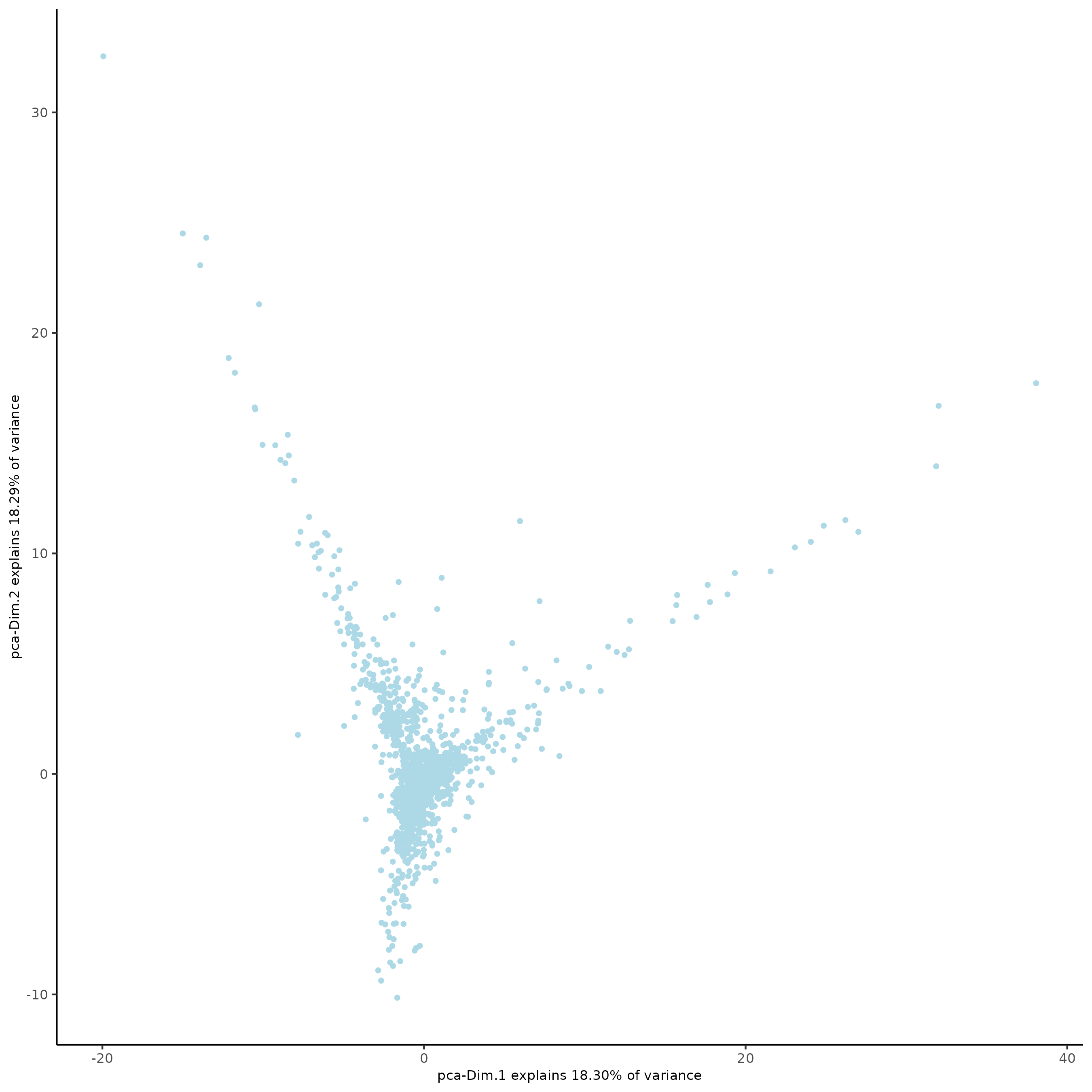
plotPCA(subc_test,
dim1_to_use = 1,
dim2_to_use = 2
)
# run UMAP
subc_test <- runUMAP(subc_test,
dimensions_to_use = 1:5,
n_threads = 2
)
plotUMAP(gobject = subc_test)
11 Cluster
subc_test <- createNearestNetwork(gobject = subc_test,
dimensions_to_use = 1:5,
k = 5
)
subc_test <- doLeidenCluster(gobject = subc_test,
resolution = 0.05,
n_iterations = 1000,
name = "leiden_0.05"
)
# Create color palettes, or proceed with Giotto defaults
devtools::install_github("alyssafrazee/RSkittleBrewer")
colorcode <- lacroix_palette(type = "paired")
featcolor <- lacroix_palette("KeyLime", type = "discrete")
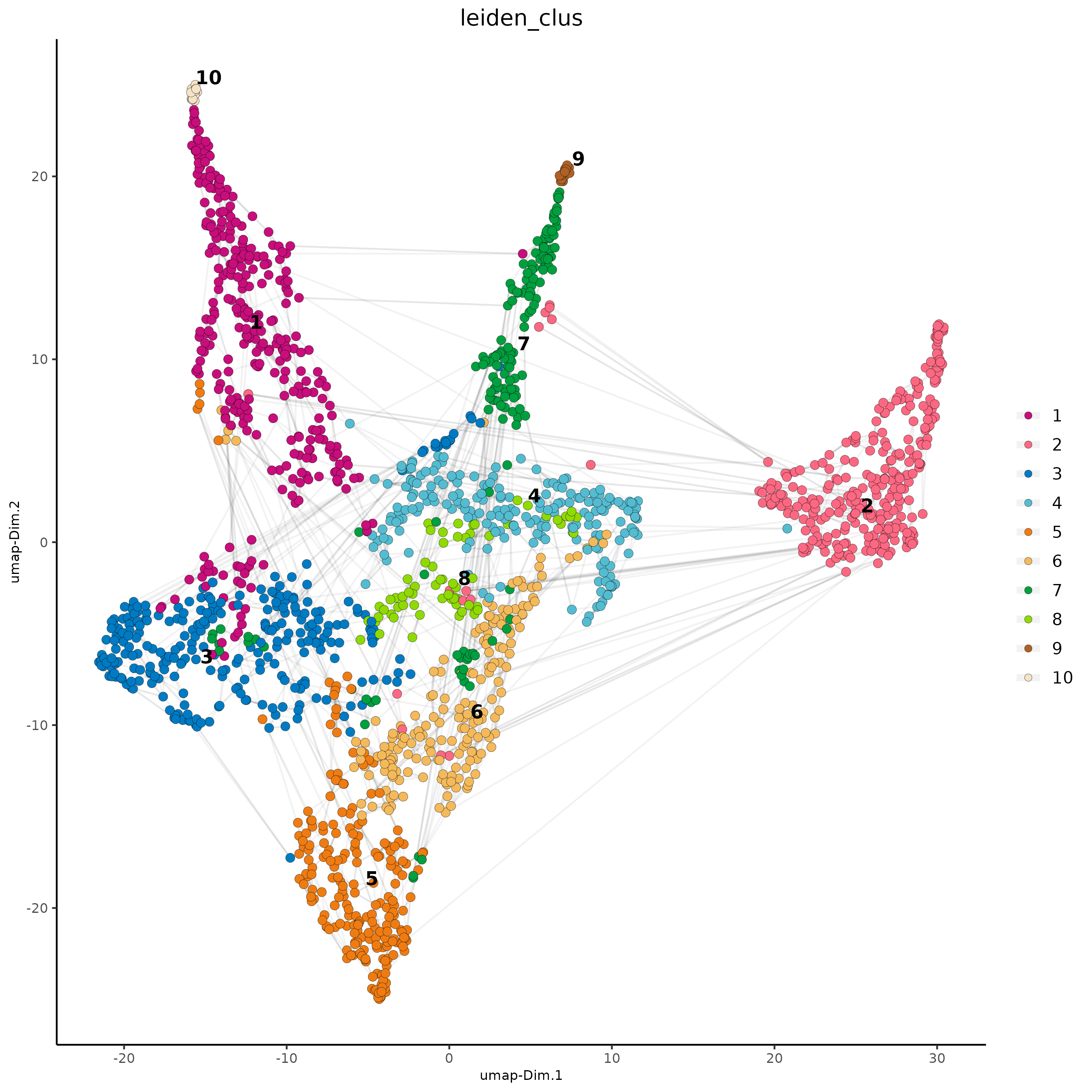
# visualize UMAP cluster results
plotUMAP(gobject = subc_test,
cell_color = "leiden_clus",
show_NN_network = TRUE,
point_size = 2.5,
cell_color_code = colorcode
)
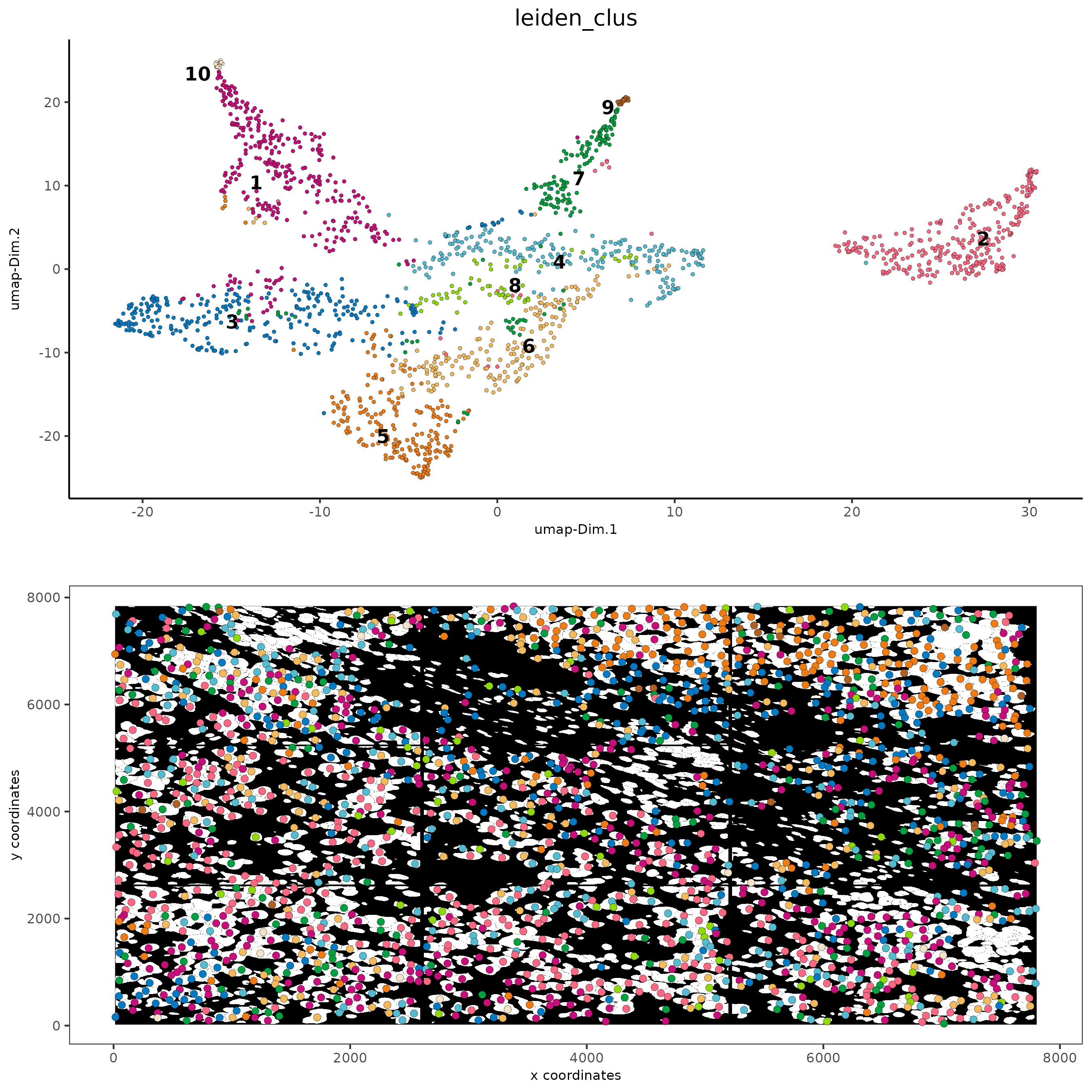
# visualize UMAP and spatial results
spatDimPlot2D(gobject = subc_test,
show_image = TRUE,
image_name = "segmentation",
cell_color = "leiden_clus",
spat_point_size = 2,
cell_color_code = colorcode
)
# Plot a cluster heatmap
showClusterHeatmap(gobject = subc_test,
cluster_column = "leiden_clus",
save_param = list(save_format = "pdf",
base_height = 6,
base_width = 8,
units = "cm")
)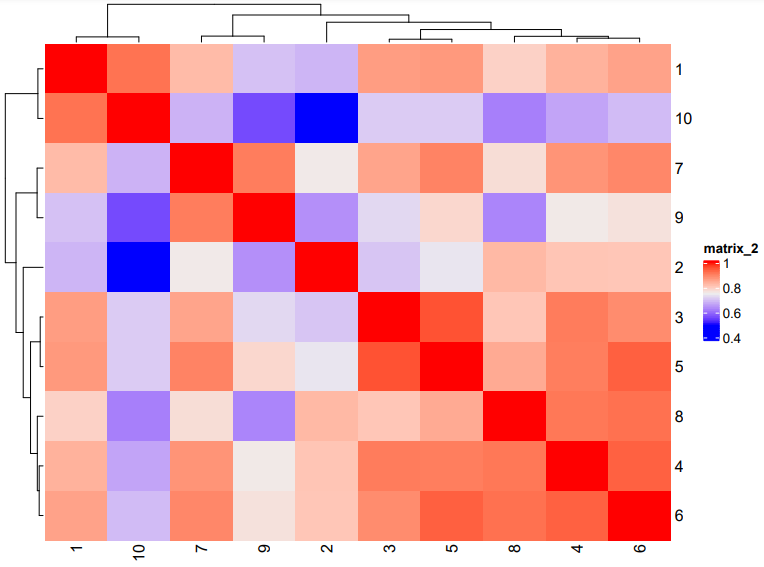
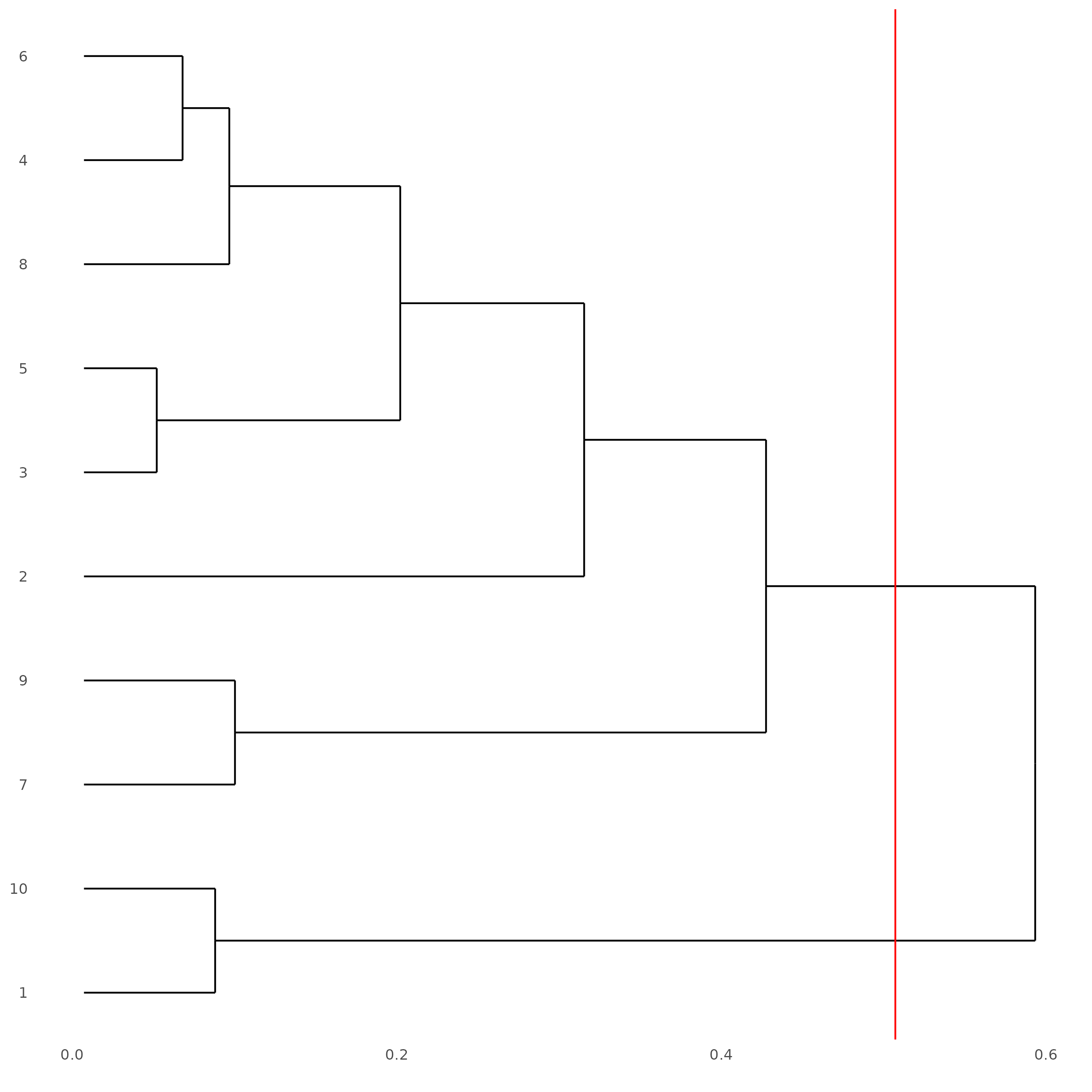
# See cluster relationships in a dendogram
showClusterDendrogram(subc_test,
h = 0.5,
rotate = TRUE,
cluster_column = "leiden_clus"
)
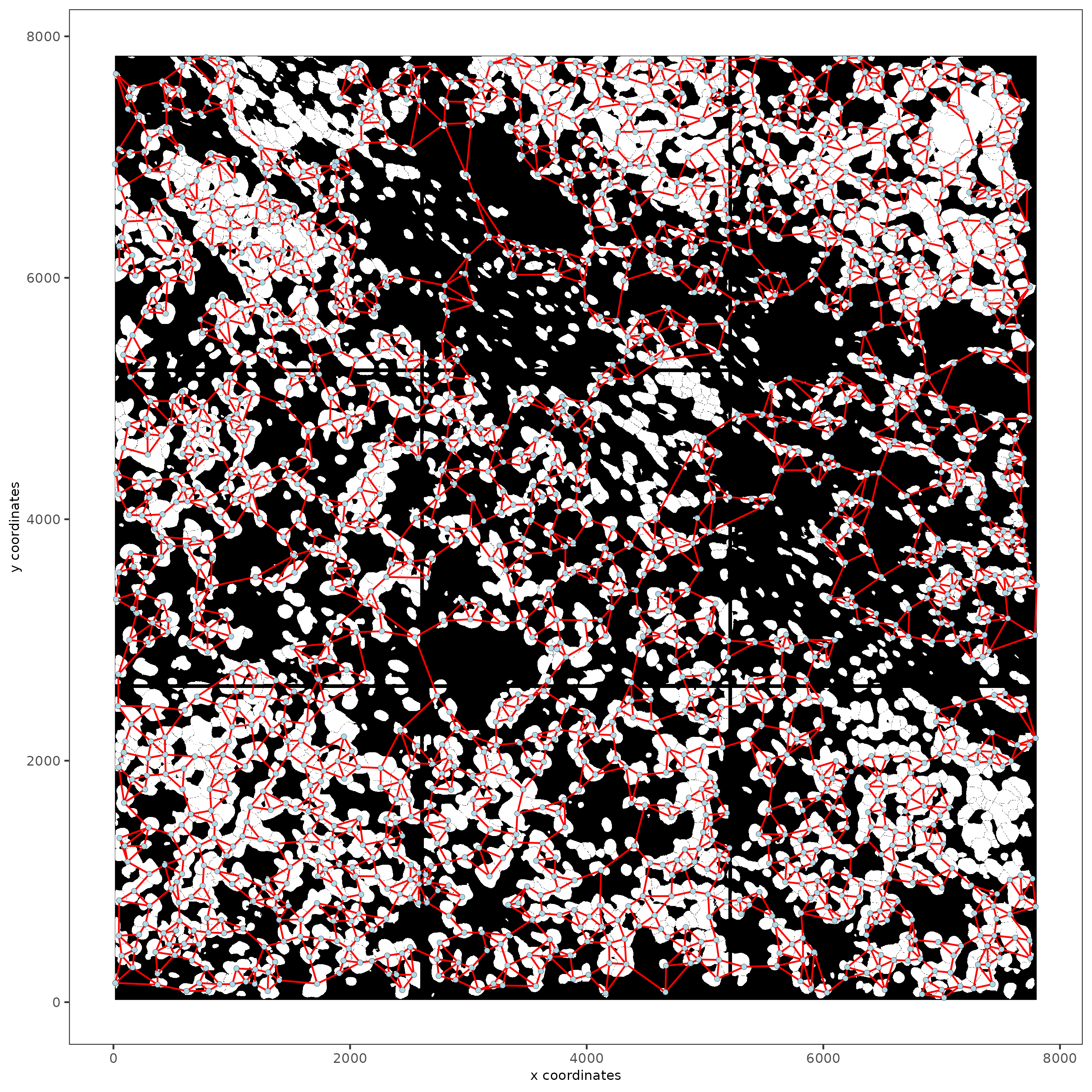
12 Create a Spatial Network
subc_test <- createSpatialNetwork(gobject = subc_test,
spat_loc_name = "cell",
minimum_k = 3,
maximum_distance_delaunay = 100
)
spatPlot2D(gobject = subc_test,
image_name = "segmentation",
show_image = TRUE,
point_size = 1.5,
show_network = TRUE
)
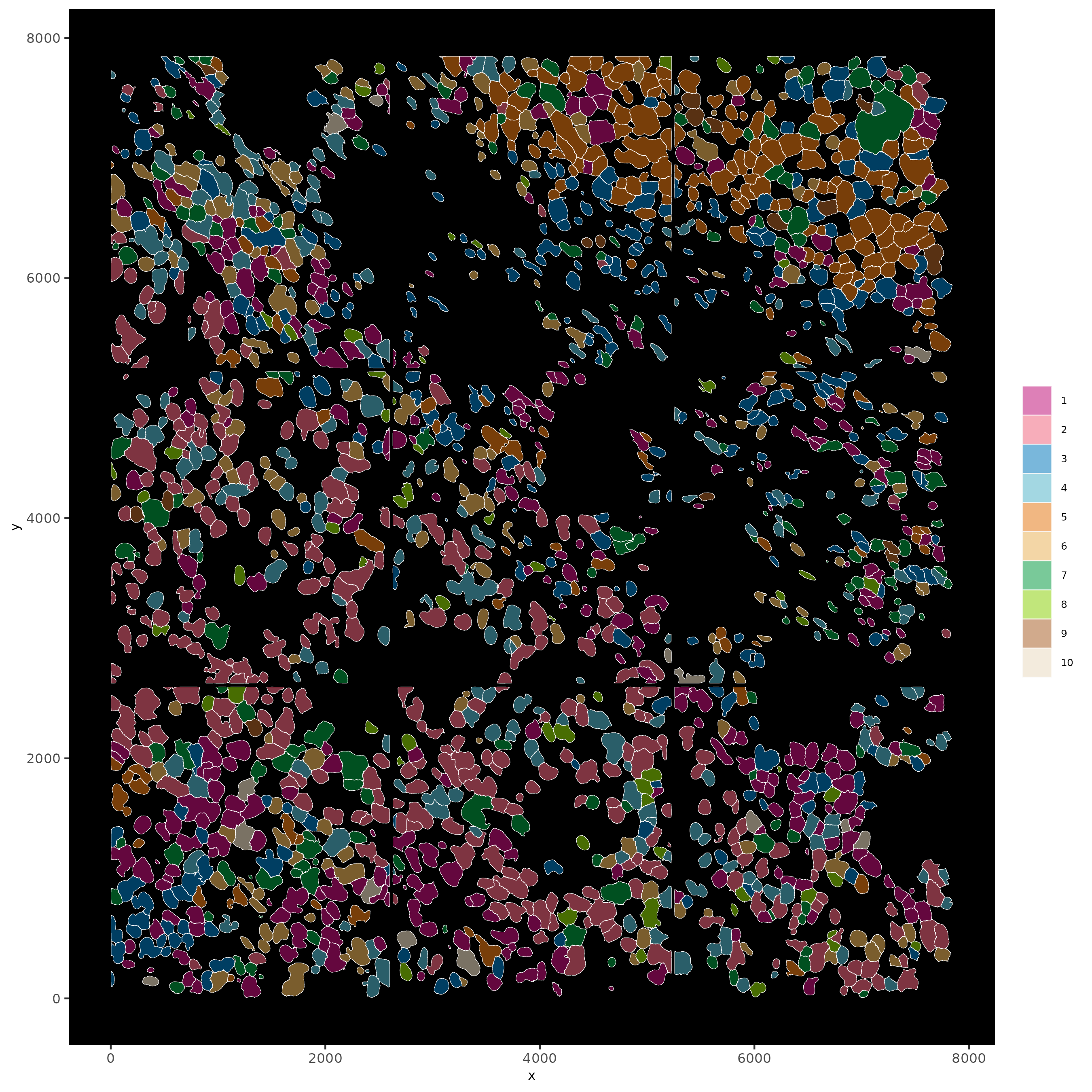
13 Visualize SubCellular Data
# Visualize clustered cells
spatInSituPlotPoints(subc_test,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1,
polygon_fill = "leiden_clus",
polygon_fill_as_factor = TRUE,
polygon_fill_code = colorcode
)
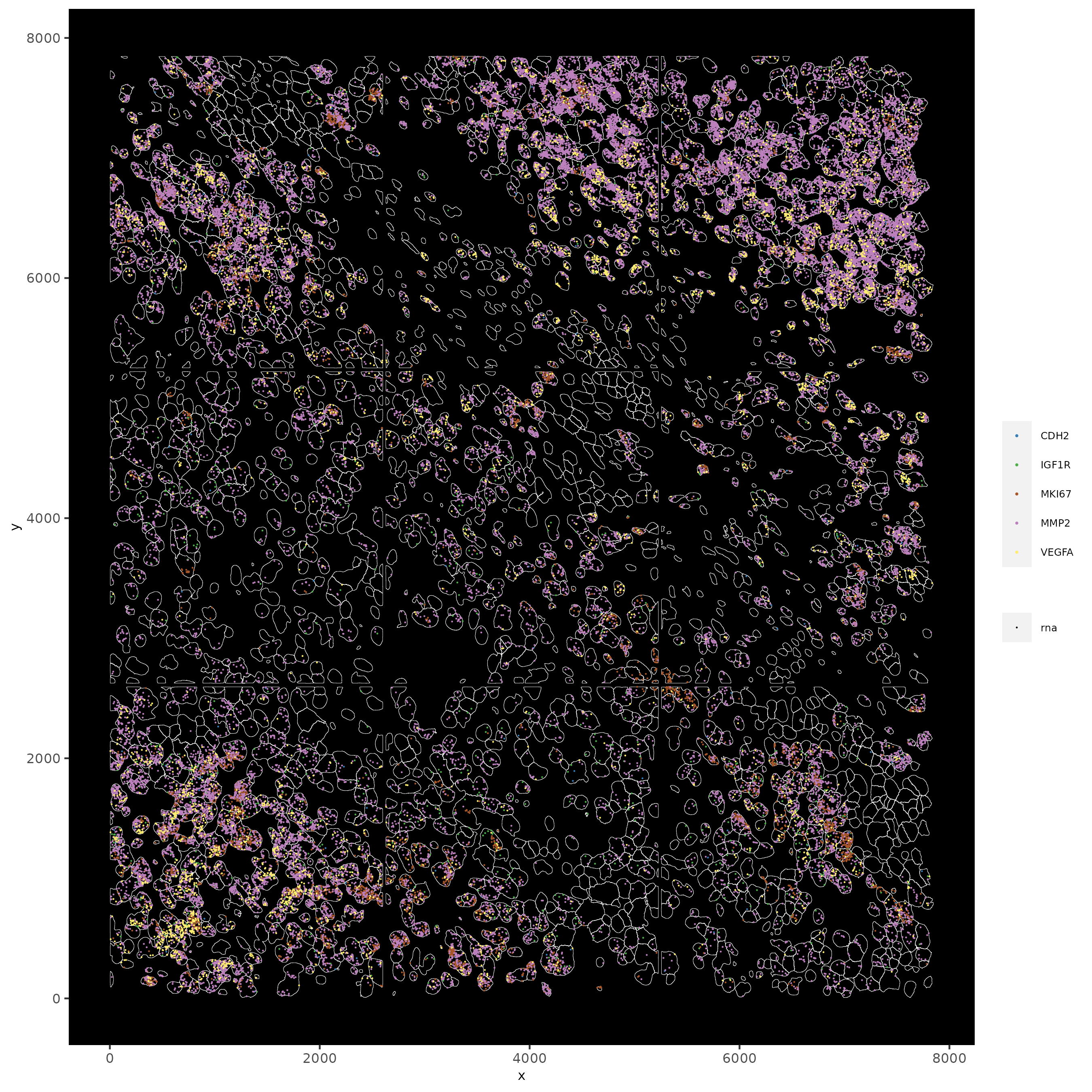
# individual plotting of transcripts and polygon information
# all cells
spatInSituPlotPoints(testobj,
feats = list("rna" = c("MMP2", "VEGFA", "IGF1R", "CDH2", "MKI67")),
point_size = 0.2,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1
)
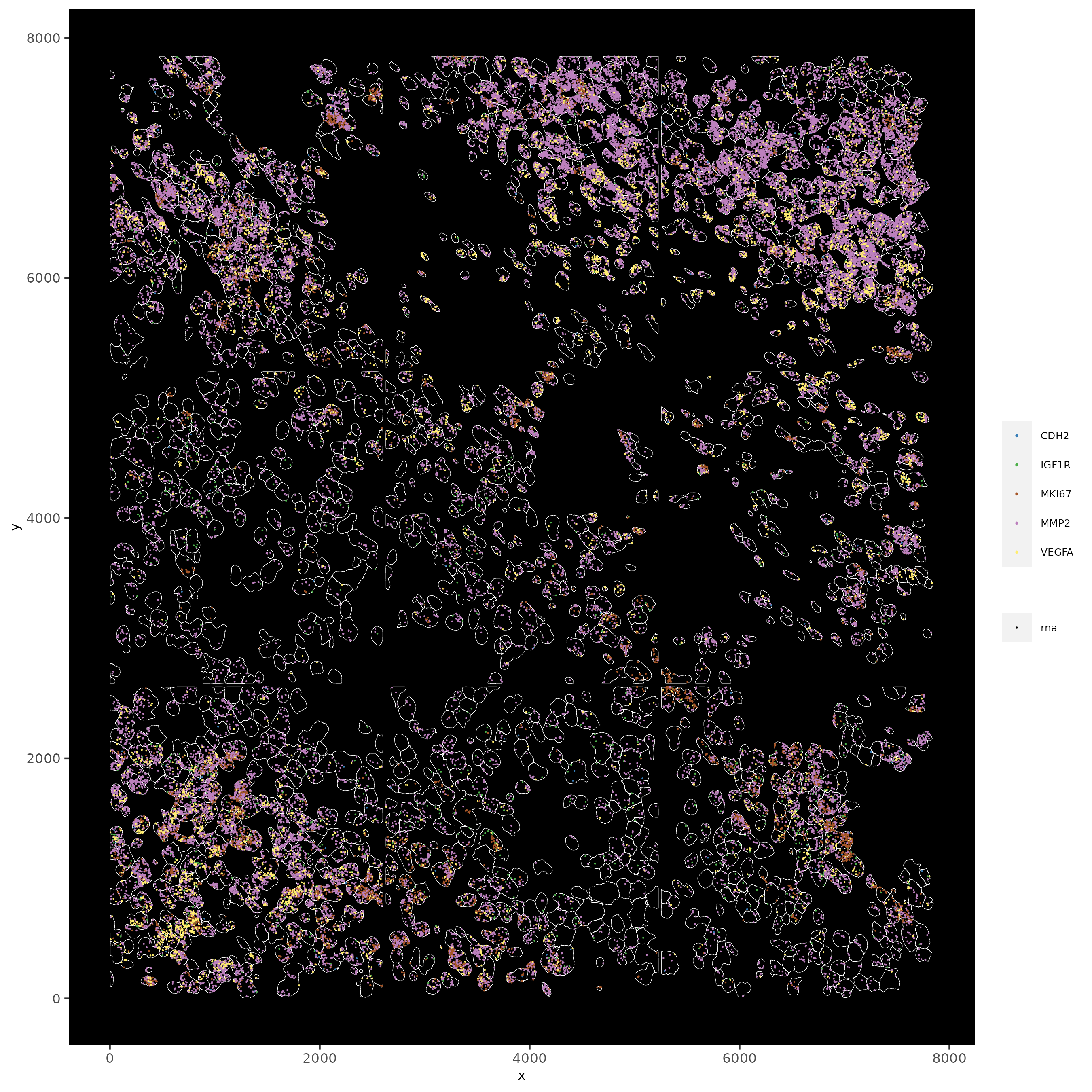
# filtered cells
spatInSituPlotPoints(subc_test,
feats = list("rna" = c("MMP2", "VEGFA", "IGF1R", "CDH2", "MKI67")),
point_size = 0.2,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1
)
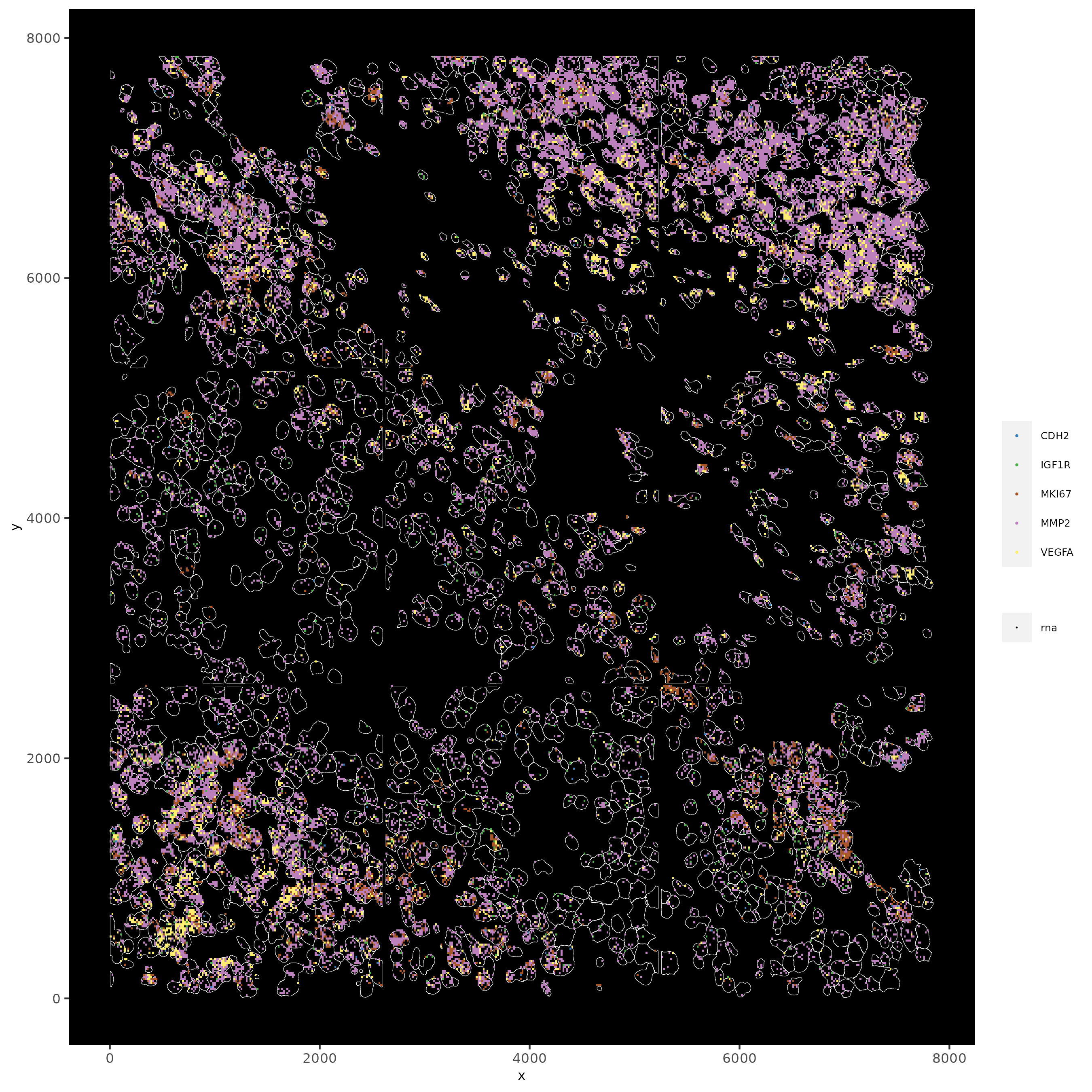
# faster plotting method if you have many points
spatInSituPlotPoints(subc_test,
plot_method = "scattermore",
feats = list("rna" = c("MMP2", "VEGFA", "IGF1R", "CDH2", "MKI67")),
point_size = 0.2,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1
)
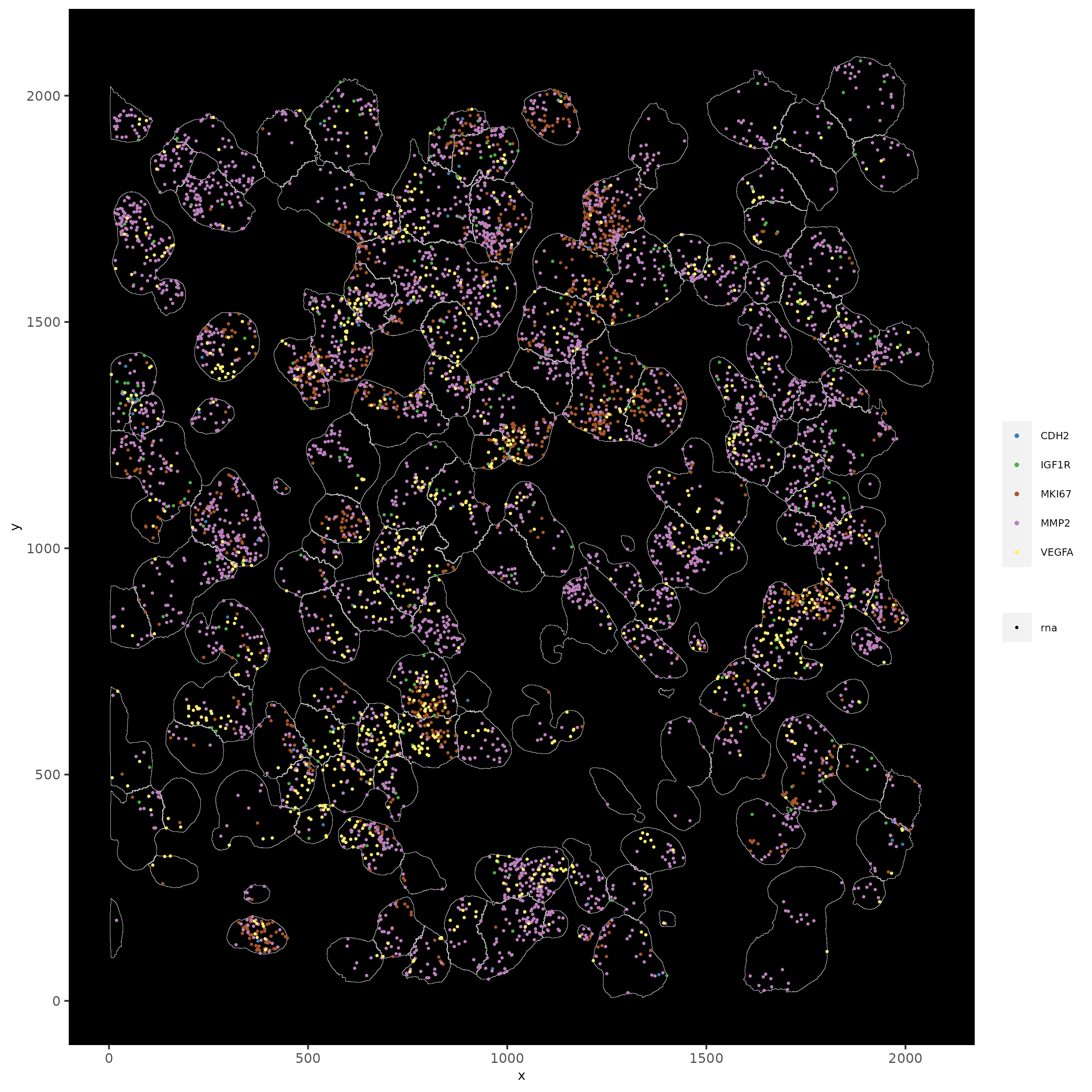
13.1 Subset by Location
# can be used to focus on specific spatial structures
# to zoom in on niche environments
subloc <- subsetGiottoLocs(subc_test,
x_min = 0, x_max = 2000,
y_min = 0, y_max = 2000,
poly_info = "cell"
)
# show subset of genes
spatInSituPlotPoints(subloc,
feats = list("rna" = c("MMP2", "VEGFA", "IGF1R", "CDH2", "MKI67")),
point_size = 0.6,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1
)
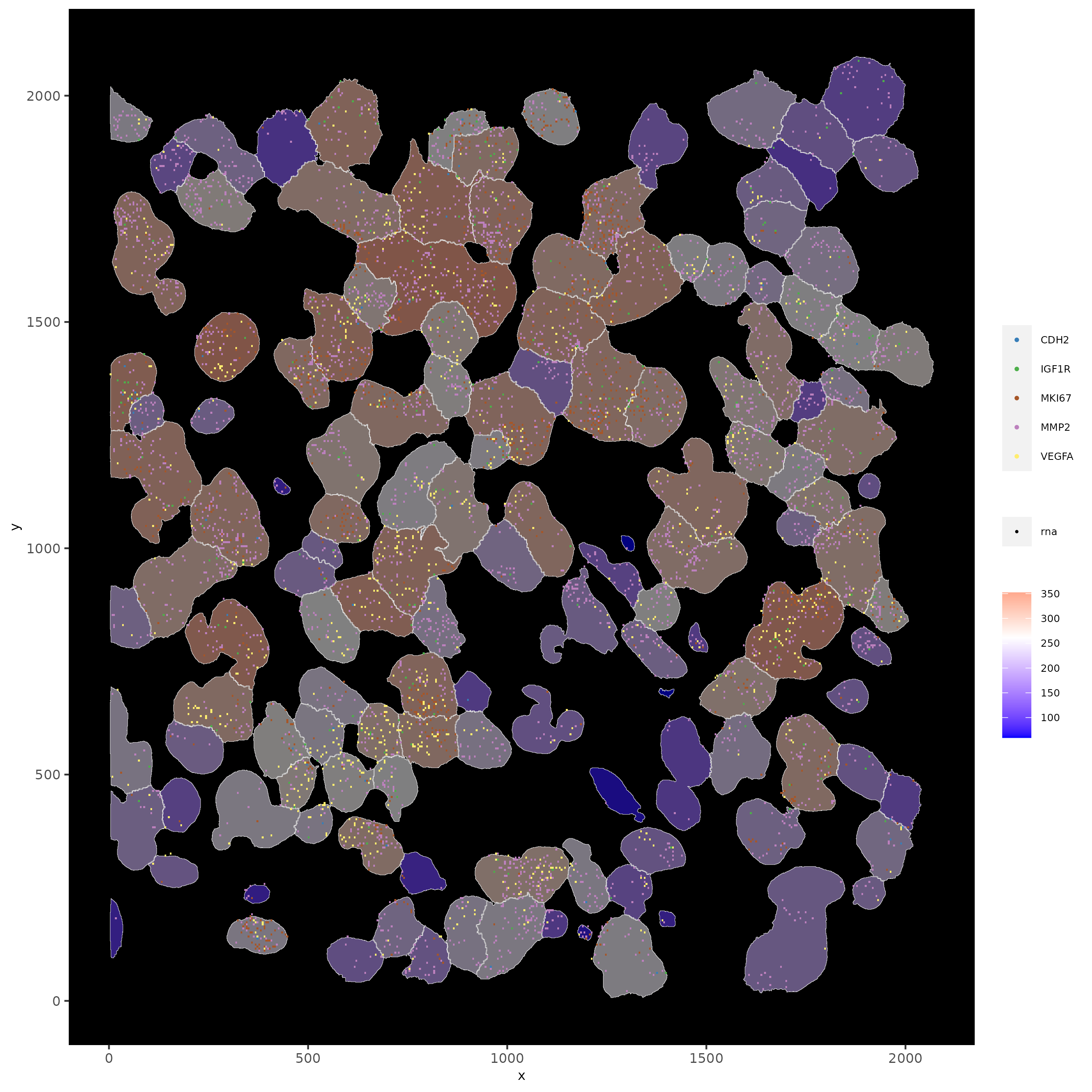
# show subset of genes and color cells according to clusters
spatInSituPlotPoints(subloc,
feats = list("rna" = c("MMP2", "VEGFA", "IGF1R", "CDH2", "MKI67")),
point_size = 0.6,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1,
polygon_fill = "leiden_clus",
polygon_fill_as_factor = TRUE,
polygon_fill_code = colorcode,
feats_color_code = featcolor
)
# show subset of genes and color cells according to total expression
# use a faster and more efficient point plotting method = scattermore
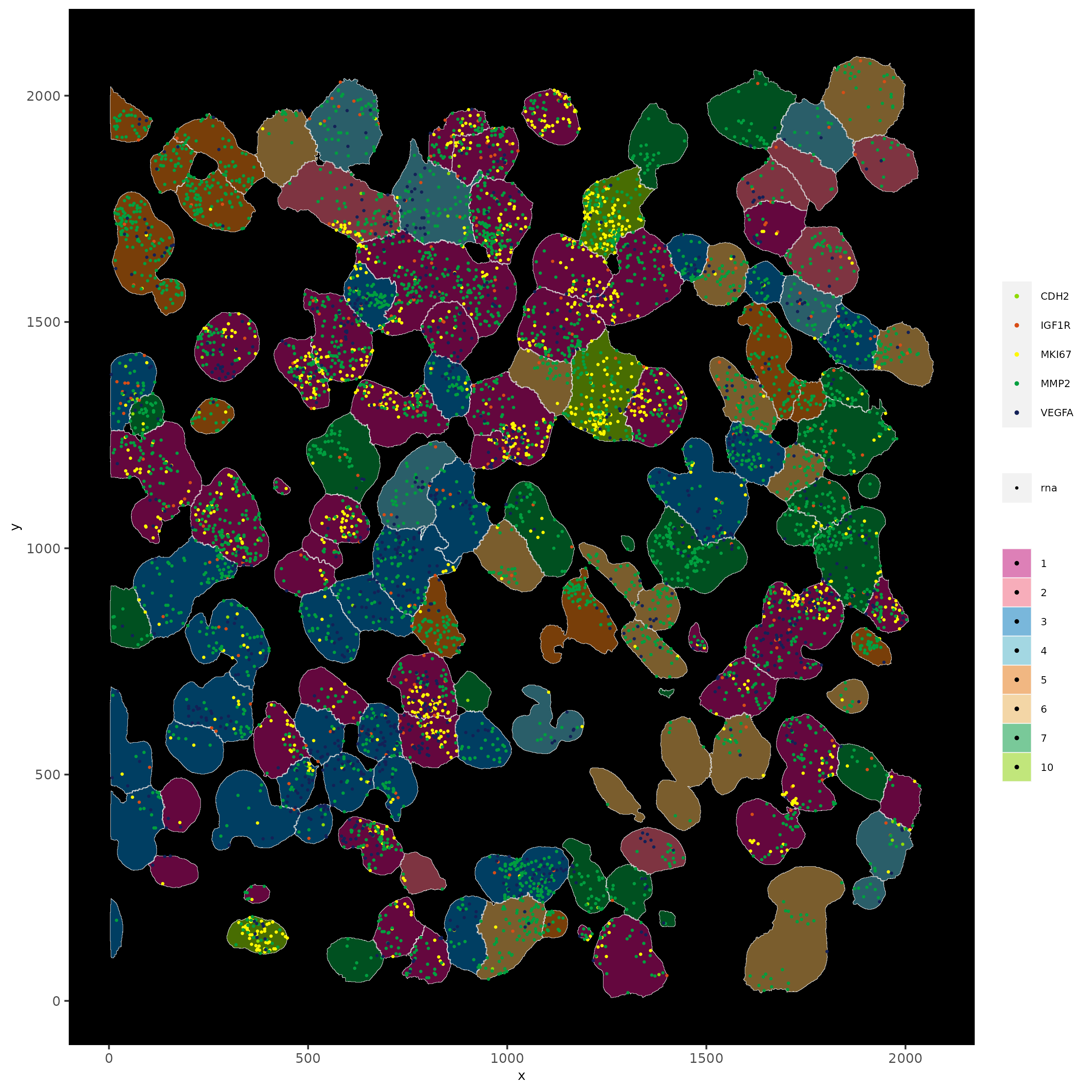
spatInSituPlotPoints(subloc,
plot_method = "scattermore",
feats = list("rna" = c("MMP2", "VEGFA", "IGF1R", "CDH2", "MKI67")),
point_size = 0.6,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1,
polygon_fill = "total_expr",
polygon_fill_as_factor = FALSE
)
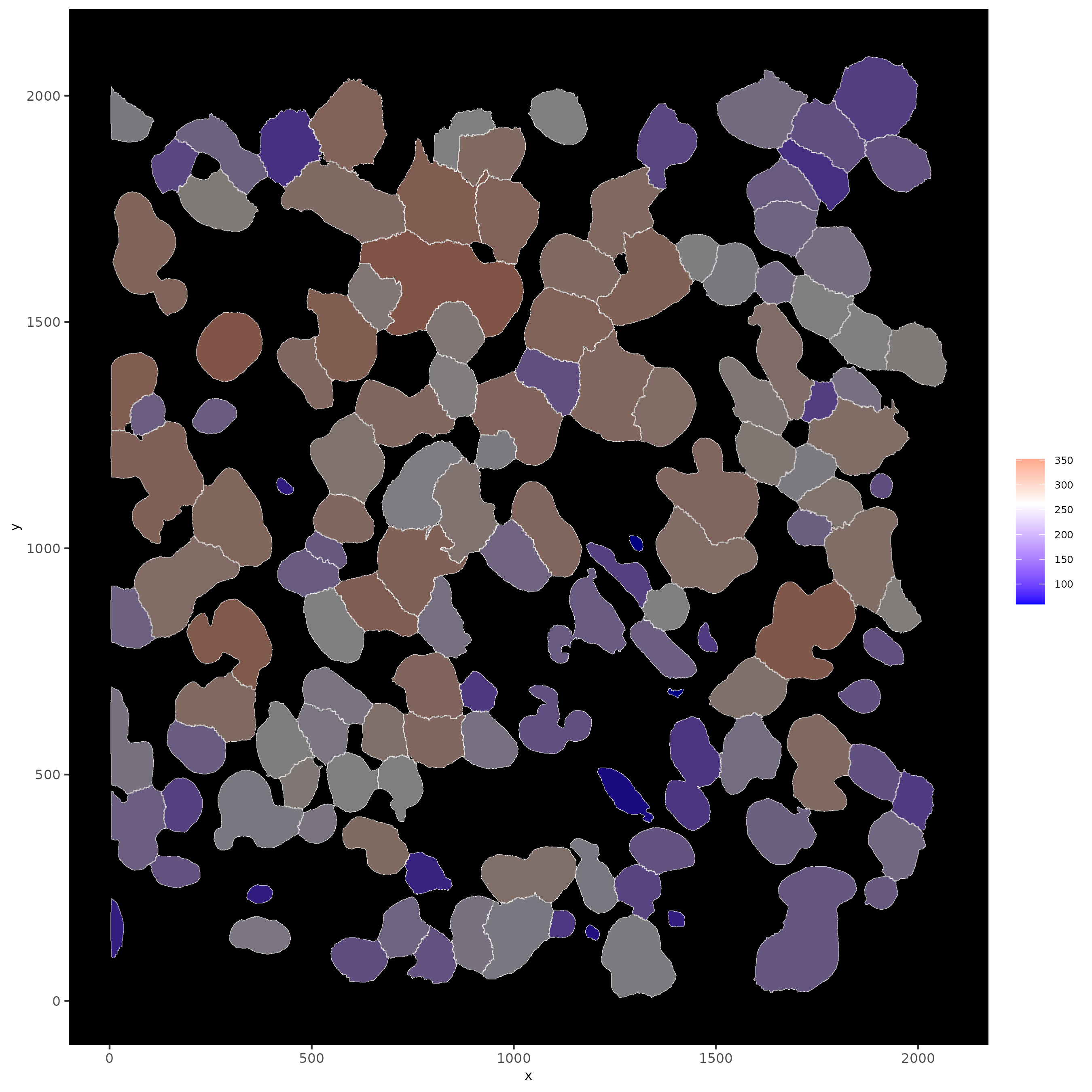
# show cells and color them according to total expression
spatInSituPlotPoints(subloc,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1,
polygon_fill = "total_expr",
polygon_fill_as_factor = FALSE
)
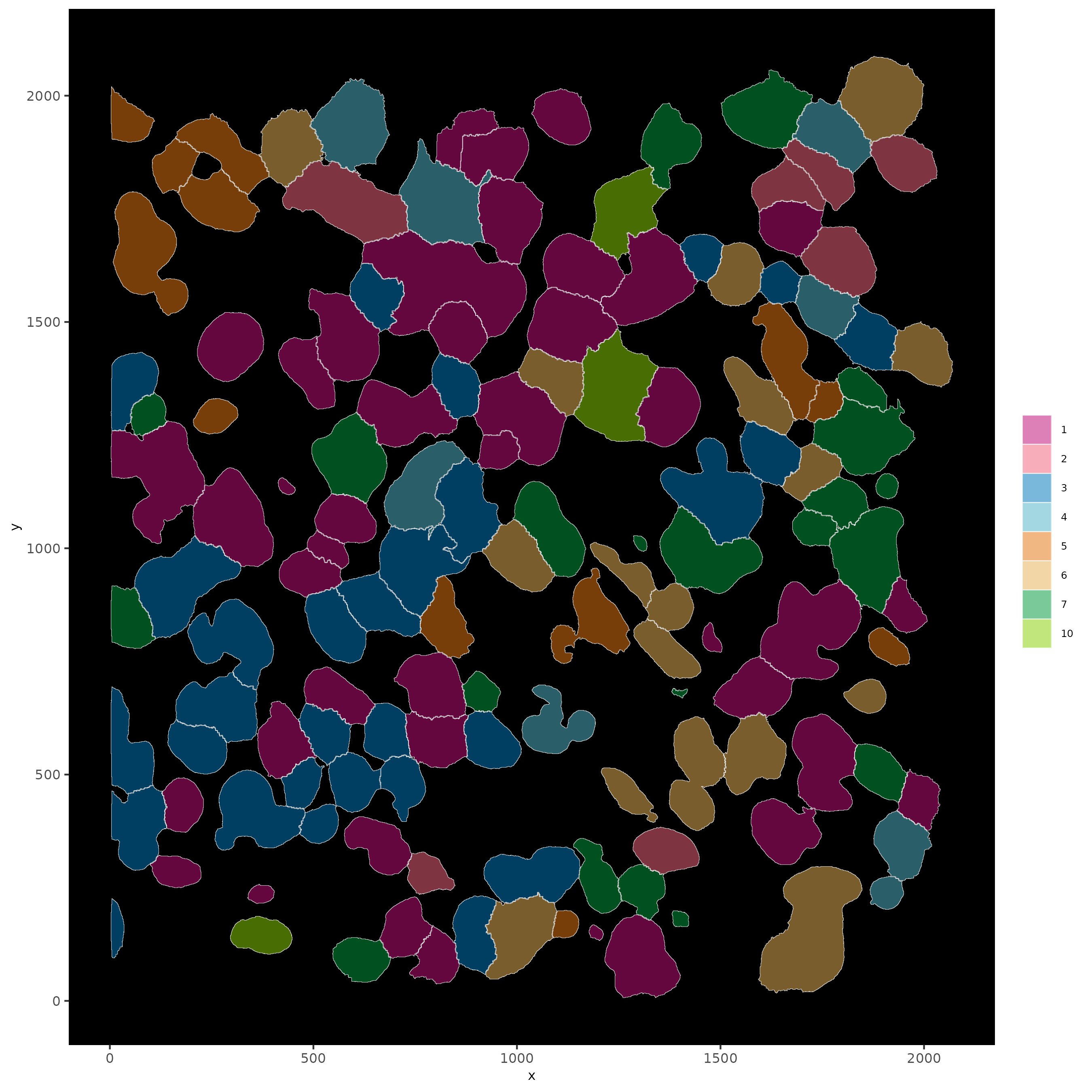
# show cells and color them according to total cluster information
spatInSituPlotPoints(subloc,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "white",
polygon_line_size = 0.1,
polygon_fill = "leiden_clus",
polygon_fill_as_factor = TRUE,
polygon_fill_code = colorcode
)
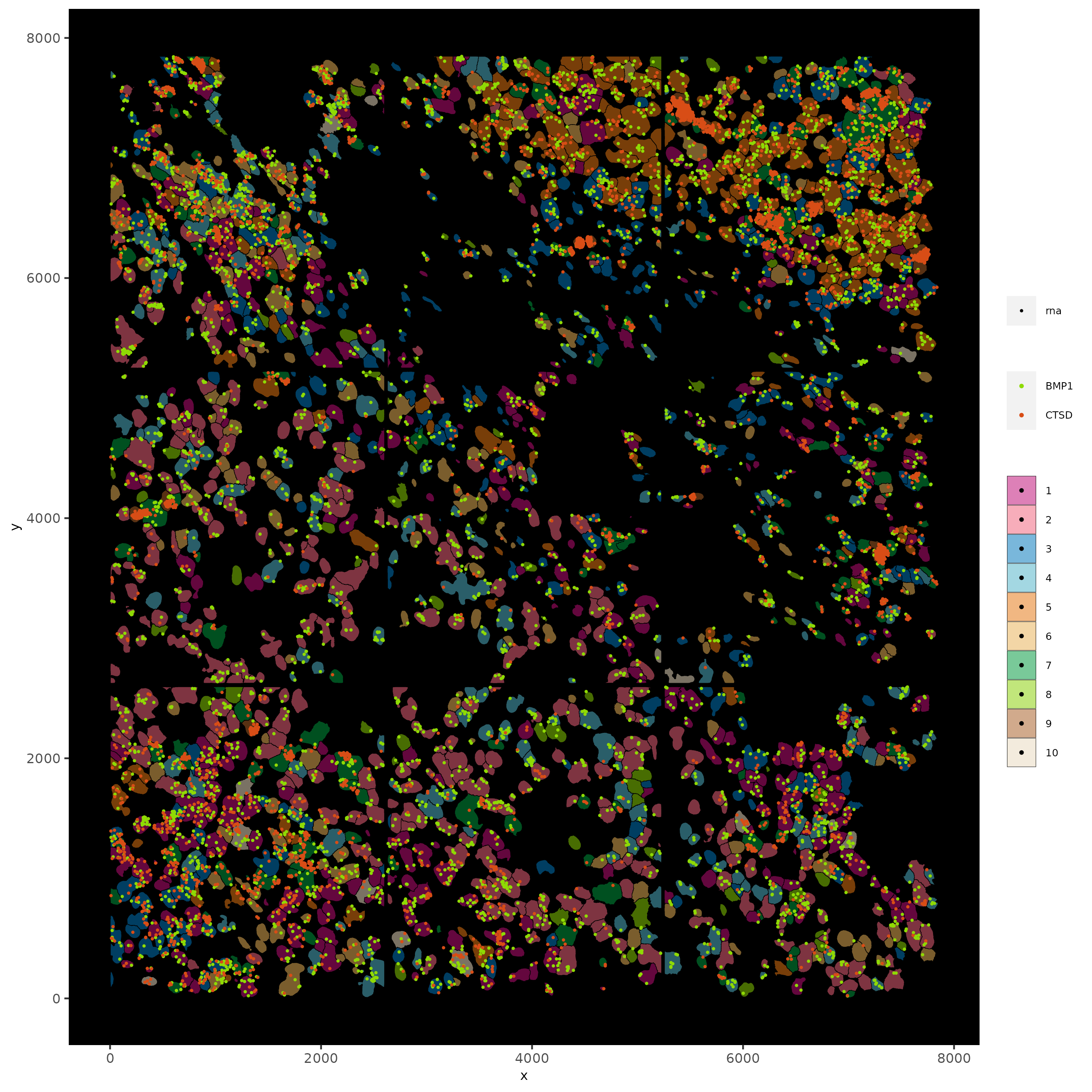
14 Find Interaction Changed Features
# find interaction changed Features
# In this case, features are genes whose expression difference is associated with a neighboring cell type
future::plan("multisession", workers = 4) # sometimes unstable, restart R session
test <- findInteractionChangedFeats(gobject = subc_test,
cluster_column = "leiden_clus"
)
test$ICFscores[type_int == "hetero"]
spatInSituPlotPoints(subc_test,
feats = list("rna" = c("CTSD", "BMP1")),
point_size = 0.6,
show_polygon = TRUE,
polygon_feat_type = "cell",
polygon_color = "black",
polygon_line_size = 0.1,
polygon_fill = "leiden_clus",
polygon_fill_as_factor = TRUE,
polygon_fill_code = colorcode,
feats_color_code = featcolor
)